Cybersecurity scientists have proposed a novel solution that leverages electromagnetic industry emanations from the Internet of Points (IoT) units as a side-channel to glean precise information about the various sorts of malware focusing on the embedded systems, even in situations where obfuscation techniques have been applied to hinder evaluation.
With the rapid adoption of IoT appliances presenting an attractive attack area for danger actors, in component due to them currently being outfitted with bigger processing ability and able of operating thoroughly useful working methods, the most recent analysis aims to boost malware analysis to mitigate probable security risks.
The findings have been introduced by a group of academics from the Investigation Institute of Computer Science, and Random Systems (IRISA) at the Yearly Personal computer Security Purposes Conference (ACSAC) held final month.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code

“[Electromagnetic] emanation that is calculated from the device is virtually undetectable by the malware,” the scientists stated in a paper. “As a result, malware evasion methods are unable to be straightforwardly applied contrary to for dynamic program monitoring. Also, given that a malware does not have command on exterior components-stage, a security procedure relying on hard]ware capabilities cannot be taken down, even if the malware owns the most privilege on the machine.”
The purpose is to choose benefit of the aspect channel details to detect anomalies in emanations when they deviate from earlier noticed styles and increase an warn when suspicious behavior emulating the malware is recorded in comparison to the system’s usual point out.
Not only does this require no modifications on the goal devices, the framework devised in the review allows the detection and classification of stealthy malware these as kernel-stage rootkits, ransomware, and distributed denial-of-support (DDoS) botnets like Mirai, counting unseen variants.
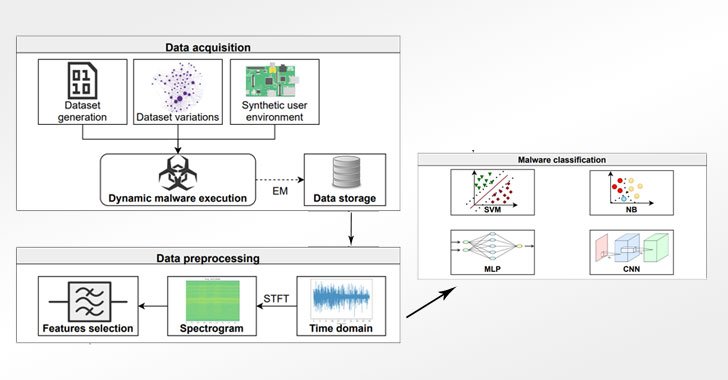
Having put around 3 phases, the side channel strategy includes measuring electromagnetic emanations when executing 30 various malware binaries as very well as undertaking benign movie, songs, photograph, and digital camera-connected pursuits to educate a convolutional neural network (CNN) product for classifying serious-environment malware samples. Specifically, the framework requires as enter an executable and outputs its malware label by entirely relying on the aspect-channel details.
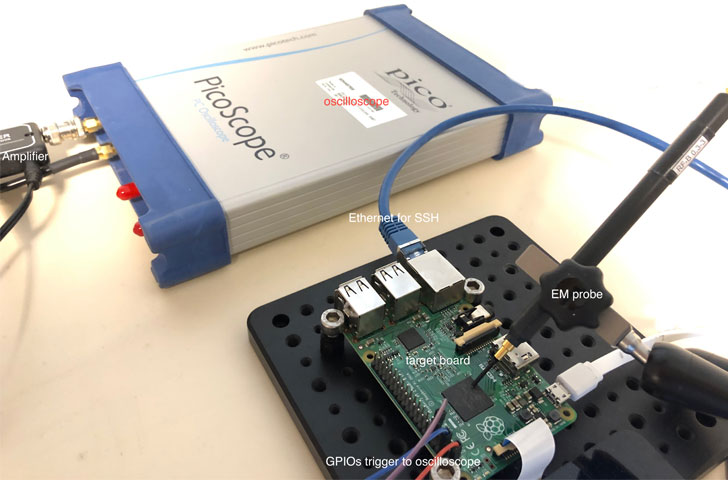
In an experimental set up, the researchers opted for a Raspberry Pi 2B as a concentrate on product with 900 MHz quad-core ARM Cortex A7 processor and 1 GB memory, with the electromagnetic indicators acquired and amplified applying a blend of an oscilloscope and a PA 303 BNC preamplifier, efficiently predicting the a few malware sorts and their related families with an accuracy of 99.82% and 99.61%.
“[B]y utilizing uncomplicated neural network versions, it is feasible to gain appreciable facts about the state of a monitored system, by observing solely its [electromagnetic] emanations,” the scientists concluded. “Our system is strong versus several code transformation/obfuscation, like random junk insertion, packing, and virtualization, even when the transformation is formerly not identified to the procedure.”
Uncovered this report exciting? Comply with THN on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn to go through a lot more exclusive content we publish.
Some sections of this report are sourced from:
thehackernews.com



 Are Medical Devices at Risk of Ransomware Attacks?
Are Medical Devices at Risk of Ransomware Attacks?