Google referred to as for contributors on Thursday to a new open resource job named Graph for Knowledge Artifact Composition (GUAC) as section of its efforts to increase application offer chain security.
In accordance to the tech large, GUAC is even now in the early stages, but it is set to improve how the industry perceives application offer chains.
“GUAC addresses a have to have produced by the burgeoning endeavours across the ecosystem to generate software package create, security, and dependency metadata,” Google wrote in a weblog article.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
“True to Google’s mission to arrange and make the world’s details universally available and practical, GUAC is intended to democratize the availability of this security information and facts by producing it freely obtainable and beneficial for every single group, not just individuals with company-scale security and IT funding.”
In accordance to Google, collaboration in groups this kind of as Open up Resource Security Foundation (OpenSSF), Provide Chain Levels for Software package Artifacts (SLSA), Software package Package Facts Trade (SPDX) and CycloneDX allows corporations to have completely ready access to a number of systems, including Computer software Bills of Resources (SBOMs), signed attestations about how program was constructed and cross-databases vulnerability databases.
“These facts are practical on their very own, but it’s tough to mix and synthesize the information for a much more comprehensive see,” reads the blog article.
“The documents are scattered across different databases and producers, are connected to diverse ecosystem entities, and can not be very easily aggregated to answer better-degree questions about an organization’s software property.”
GUAC has been established to tackle these issues by bringing with each other several distinctive sources of software security metadata, also thanks to partnerships concerning the tech large, Kusari, Purdue College and Citi.
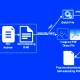
From a specialized standpoint, GUAC has four main spots of features: selection of metadata from a variety of resources of software package security databases, ingestion of said facts, collation into a coherent graph and querying for a presented artifact to view its SBOM, provenance, create chain, job scorecard, vulnerabilities, and so on.
“GUAC aggregates and synthesizes software security metadata at scale and tends to make it meaningful and actionable,” Google wrote.
“We’re energized to share the project’s evidence of idea, which allows you question a little dataset of software metadata, like SLSA provenance, SBOMs, and OpenSSF Scorecards.”
The development of GUAC arrives months after Google introduced a new program made to reward scientists that locate bugs in its open up resource assignments.
Some areas of this posting are sourced from:
www.infosecurity-magazine.com


 Thousands of Publicly Exposed API Tokens Could Threaten Software Integrity
Thousands of Publicly Exposed API Tokens Could Threaten Software Integrity