Destructive actors such as Kinsing are using edge of the two not too long ago disclosed and older security flaws in Oracle WebLogic Server to provide cryptocurrency-mining malware.
Cybersecurity corporation Pattern Micro mentioned it identified the financially-inspired group leveraging the vulnerability to drop Python scripts with capabilities to disable working program (OS) security characteristics these as Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux), and many others.
The operators at the rear of the Kinsing malware have a history of scanning for vulnerable servers to co-opt them into a botnet, together with that of Redis, SaltStack, Log4Shell, Spring4Shell, and the Atlassian Confluence flaw (CVE-2022-26134).

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount

The Kinsing actors have also been concerned in strategies from container environments via misconfigured open up Docker Daemon API ports to launch a crypto miner and subsequently distribute the malware to other containers and hosts.
The newest wave of attacks involves the actor weaponizing CVE-2020-14882 (CVSS score: 9.8), a two-year-outdated distant code execution (RCE) bug, against unpatched servers to seize control of the server and drop destructive payloads.
It can be well worth noting that the vulnerability has been exploited in the previous by multiple botnets to distribute Monero miners and the Tsunami backdoor on contaminated Linux programs.
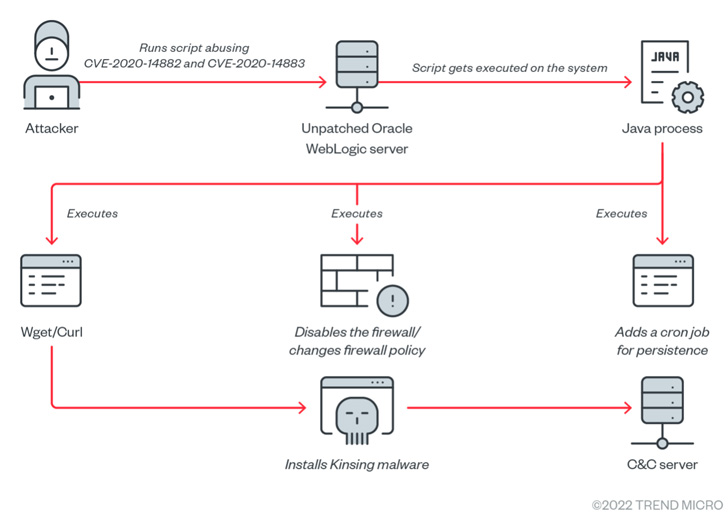
Thriving exploitation of the flaw was succeeded by the deployment of a shell script that is responsible for a series of actions: Removing the /var/log/syslog technique log, turning off security options and cloud support agents from Alibaba and Tencent, and killing competing miner procedures.
The shell script then proceeds to obtain the Kinsing malware from a remote server, whilst also getting steps to ensure persistence by suggests of cron work.
“The profitable exploitation of this vulnerability can guide to RCE, which can let attackers to accomplish a myriad of malicious routines on influenced programs,” Trend Micro mentioned. “This can range from malware execution […] to theft of critical data, and even total manage of a compromised device.”
TeamTNT actors make a comeback with the Kangaroo Attack
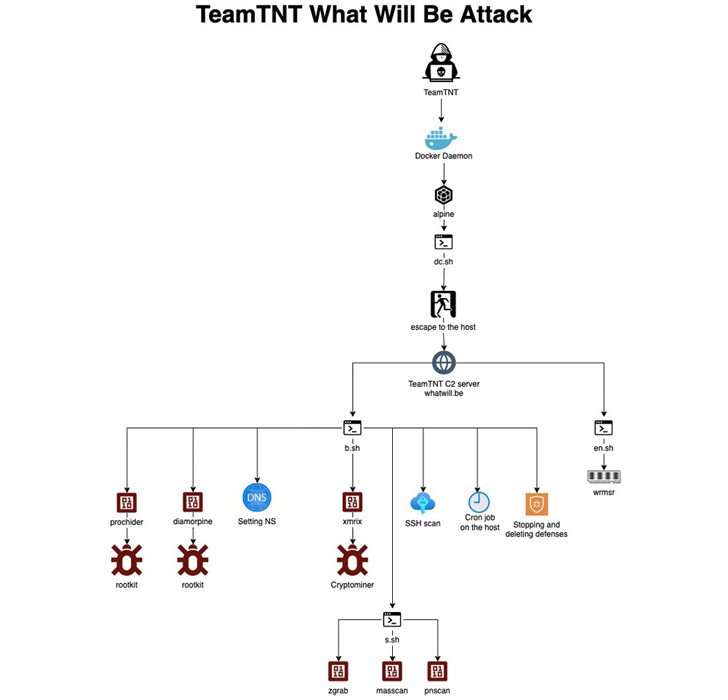
The improvement will come as researchers from Aqua Security discovered three new attacks connected to yet another “vivid” cryptojacking group named TeamTNT, which voluntarily shut store in November 2021.
“TeamTNT has been scanning for a misconfigured Docker Daemon and deploying alpine, a vanilla container graphic, with a command line to download a shell script (k.sh) to a C2 server,” Aqua Security researcher Assaf Morag reported.
What is noteworthy about the attack chain is that it appears to be made to crack SECP256K1 encryption, which, if successful, could give the actor the ability to compute the keys to any cryptocurrency wallet. Put in different ways, the strategy is to leverage the superior but illegal computational ability of its targets to run the ECDLP solver and get the essential.

Two other attacks mounted by the team entail the exploitation of uncovered Redis servers and misconfigured Docker APIs to deploy coin miners and Tsunami binaries.
TeamTNT’s targeting of Docker Relaxation APIs has been nicely-documented around the previous year. But in an operational security blunder spotted by Craze Micro, qualifications connected with two of the attacker-controlled DockerHub accounts have been uncovered.
The accounts – alpineos and sandeep078 – are explained to have been made use of to distribute a variety of destructive payloads like rootkits, Kubernetes exploit kits, credential stealers, XMRig Monero miners, and even the Kinsing malware.
“The account alpineos was used in exploitation tries on our honeypots 3 occasions, from mid-September to early October 2021, and we tracked the deployments’ IP addresses to their site in Germany,” Development Micro’s Nitesh Surana reported.
“The danger actors were logged in to their accounts on the DockerHub registry and most likely forgot to log out.” Alternatively, “the risk actors logged in to their DockerHub account applying the credentials of alpineos.”
Craze Micro said the malicious alpineos picture had been downloaded a lot more than 150,000 periods, including it notified Docker about these accounts.
It is also recommending corporations to configure the exposed Rest API with TLS to mitigate adversary-in-the-center (AiTM) attacks, as perfectly as use credential merchants and helpers to host consumer credentials.
Observed this write-up fascinating? Follow THN on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn to examine extra exceptional information we write-up.
Some elements of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Allies Warn of Iranian Ransom Attacks Using Log4Shell
Allies Warn of Iranian Ransom Attacks Using Log4Shell