An unofficial security patch has been created available for a new Windows zero-day vulnerability in the Microsoft Assist Diagnostic Instrument (MSDT), even as the Follina flaw proceeds to be exploited in the wild.
The issue — referenced as DogWalk — relates to a path traversal flaw that can be exploited to stash a destructive executable file to the Windows Startup folder when a prospective target opens a specifically crafted “.diagcab” archive file that consists of a diagnostics configuration file.
The strategy is that the payload would get executed the subsequent time the sufferer logs in to the method soon after a restart. The vulnerability impacts all Windows versions, setting up from Windows 7 and Server Server 2008 to the latest releases.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount

DogWalk was at first disclosed by security researcher Imre Rad in January 2020 right after Microsoft, acquiring acknowledged the issue, deemed it as not a security issue.
“There are a variety of file sorts that can execute code in this sort of a way but aren’t technically ‘executables,'” the tech large reported at the time. “And a variety of these are deemed unsafe for end users to obtain/obtain in email, even ‘.diagcab’ is blocked by default in Outlook on the web and other areas.”
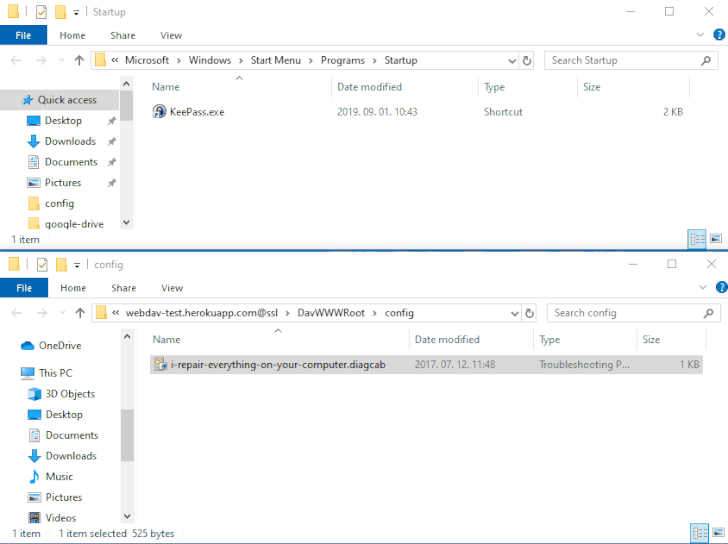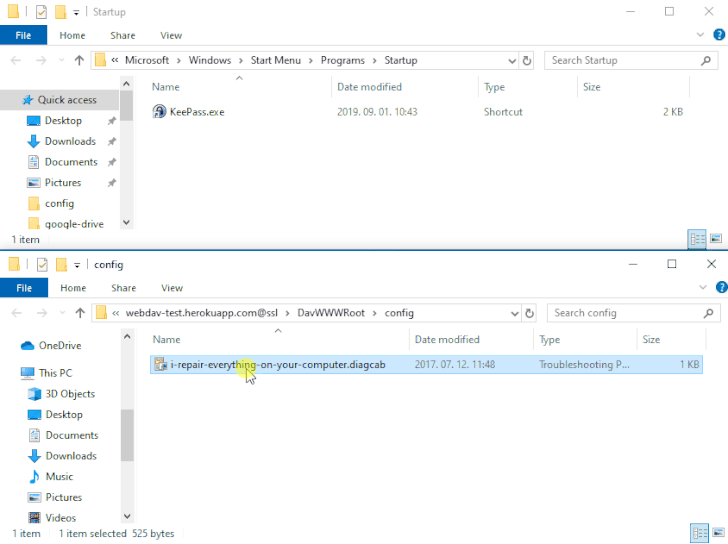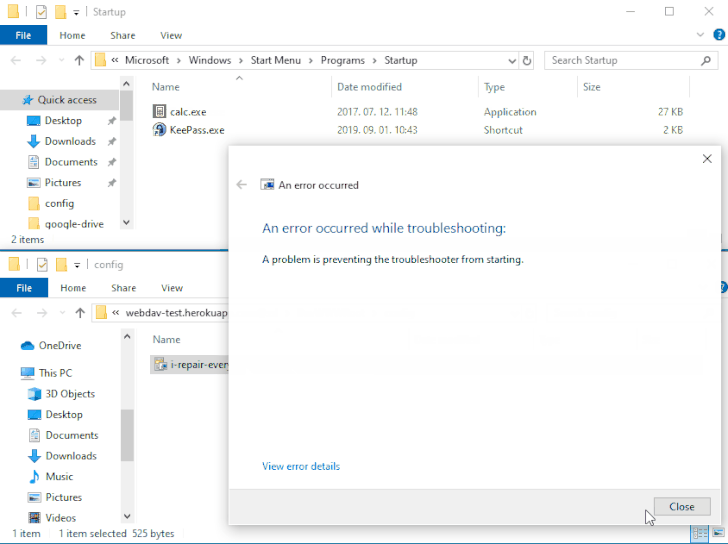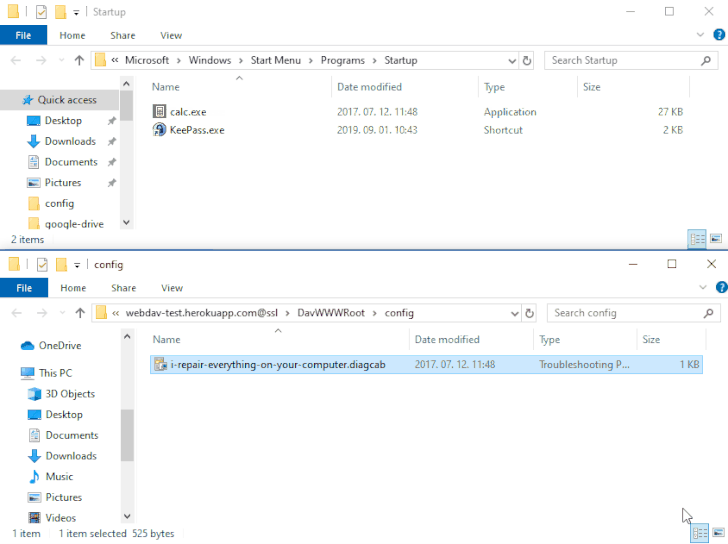
Even though all information downloaded and been given by using email consist of a Mark-of-the-Web (MOTW) tag that is utilised to decide their origin and induce an suitable security reaction, 0patch’s Mitja Kolsek noted that the MSDT software is not developed to look at this flag and for this reason enables the .diagcab file to be opened with no warning.
“Outlook is not the only supply car or truck: these types of file is cheerfully downloaded by all key browsers like Microsoft Edge by only going to(!) a internet site, and it only requires a one click (or mis-simply click) in the browser’s downloads checklist to have it opened,” Kolsek reported.
“No warning is demonstrated in the system, in contrast to downloading and opening any other known file able of executing [the] attacker’s code.”
The patches and the renewed desire in the zero-day bug follow energetic exploitation of the “Follina” distant code execution vulnerability by leveraging malware-laced Term paperwork that abuse the “ms-msdt:” protocol URI scheme.

In accordance to business security company Proofpoint, the flaw (CVE-2022-30190, CVSS score: 7.8) is becoming weaponized by a danger actor tracked as TA570 to supply the QBot (aka Qakbot) information and facts-stealing trojan.
“Actor utilizes thread hijacked messages with HTML attachments which, if opened, drop a ZIP archive,” the firm claimed in a series of tweets detailing the phishing attacks.
“Archive includes an IMG with a Term doc, shortcut file, and DLL. The LNK will execute the DLL to begin QBot. The doc will load and execute a HTML file containing PowerShell abusing CVE-2022-30190 utilized to download and execute Qbot.”
QBot has also been employed by first accessibility brokers to obtain first accessibility to concentrate on networks, enabling ransomware affiliates to abuse the foothold to deploy file-encrypting malware.
The DFIR Report, before this 12 months, also documented how QBot infections shift at a rapid tempo, enabling the malware to harvest browser info and Outlook email messages a mere 30 minutes after first obtain and propagate the payload to an adjacent workstation close to the 50-minute mark.
Observed this write-up fascinating? Observe THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to read through extra distinctive articles we post.
Some pieces of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 #RSAC: How the US Government and Industry Work Together to Stop Cyber-Attacks
#RSAC: How the US Government and Industry Work Together to Stop Cyber-Attacks