Cyber extortion remains a top threat, but its geographical get to is shifting, Orange Cyberdefense (OCD) observed in the Security Navigator 2023, the most recent version of its once-a-year report on the risk landscape, introduced on December 1, 2022.
The report shows that cyber extortion, a classification specified ‘Cy-X’ by OCD signifies the compromise of some belongings from a corporate network for ransom and includes ransomware, ranks as the quantity a single variety of cyberattack.
This kind of attacks accounted for a significant bulk of the 29,291 incidents the report was in a position to verify, Charl van der Walt, head of OCD’s Security Research Centre and direct writer of the report, instructed Infosecurity.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
Cyber Extortion Surges in China
Having said that, Van der Walt’s crew saw a significant geographic shift in victims of cyber extortion.
“Large English-talking countries have generally been the most impacted by cyber extorsion, principally mainly because of the sizing of their economic climate and the easy accessibility their businesses offer you to cyber-criminals,” Van der Walt recalled.
“More commonly, we are certain that victims’ geographics tracks GDP, with the exception of India, China and Japan owing to language and cultural ‘barriers’,” he additional.
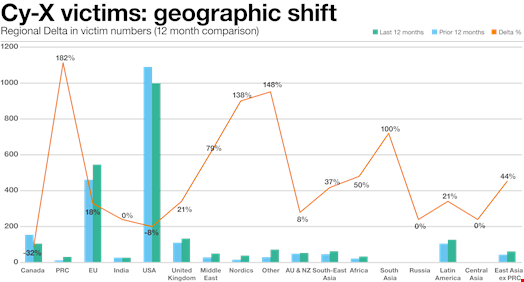
While 7 of the 10 countries with the most victims of extortion in the Security Navigator 2023 aligned with the world’s most significant economies, many areas outside of the English-speaking areas are now currently being hit.
OCD reported US-centered Cy-X volumes down 8% in the final 12 months and down 32% in Canada. The EU and the UK continued to see their cyber extortion victims increase by 18% and 21%.
The most sizeable development, however, can be found in Africa (+50%), the Middle East (+79%) and South Asia (+100%). China on your own noticed an boost of 182% in victims of Cy-X involving 2021 and 2022.
Businesses’ Security Would seem to Be Getting Improved
The report also identified that general cyber incidents amplified by 5% globally among 2021 and 2022. “This great information, as very last year’s raise was larger (+13%),” Hugues Foulon, OCD’s CEO, said throughout the launching event in Lyon on November 25, 2022.
In accordance to Van der Walt, “it means that, by some steps, our clients’ security seems to be obtaining improved.”
The researcher claimed that this enhancement can mainly be attributed to “enhanced penetration tests and the development in and improved sophistication of security resources this sort of as endpoint detection and reaction (EDR) methods.”
“We are not declaring there is considerably less action, but less drama for the clientele.”Charl van der Walt, head of security study, Orange Cyberdefense
This year’s report reveals that of 99,506 probable cybersecurity incidents, 29,291 have been confirmed. “This signifies a decrease of 17.7% of verified cyber incidents when compared with 2021’s knowledge, which signifies that, for the same amount of spend, the customer is now working with much more exact, extra precise factors and much less very low signals,” Van der Walt informed Infosecurity.
“We’re not expressing there is much less action, but much less drama for the clients,” he extra.
 Source: Orange Cyberdefense
Source: Orange Cyberdefense
Production Continues to be the Most Impacted Sector
Other conclusions of the report display that phishing proceeds to be the selection one particular vector of compromise and malware the main corruption tool, accounting for 40% of cyber incidents – and up to 43% for huge businesses and 49% for SMEs.
In the same way, the manufacturing field remains the most impacted sector in phrases of victim count.
This position is especially stressing, “given that manufacturing is a comparatively modest marketplace,” Van der Walt observed.
“This could be due to the fact industrial organizations are more focused but also due to the fact they are not paying out as significantly as other sectors, which entices menace actors to publish the hacks. We only see the details that either party wishes to share – not the negotiations guiding closed doorways,” he included.
Some pieces of this report are sourced from:
www.infosecurity-journal.com


 Google Releases Chrome Emergency Fix
For Ninth Zero-Day This Year
Google Releases Chrome Emergency Fix
For Ninth Zero-Day This Year