A malware botnet termed Ebury is estimated to have compromised 400,000 Linux servers since 2009, out of which a lot more than 100,000 have been continue to compromised as of late 2023.
The results arrive from Slovak cybersecurity agency ESET, which characterized it as a person of the most superior server-facet malware strategies for fiscal obtain.
“Ebury actors have been pursuing monetization functions […], which include the distribute of spam, web traffic redirections, and credential thieving,” security researcher Marc-Etienne M.Léveillé explained in a deep dive assessment.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
“[The] operators are also concerned in cryptocurrency heists by working with AitM and credit history card thieving by using network traffic eavesdropping, normally recognized as server-side web skimming.”
Ebury was first documented about a ten years back as aspect of a campaign codenamed Procedure Windigo that qualified Linux servers to deploy the malware, together with other backdoors and scripts like Cdorked and Calfbot to redirect web website traffic and mail spam, respectively.

Subsequently, in August 2017, a Russian nationwide named Maxim Senakh was sentenced to nearly four years in jail in the U.S. for his role in the progress and servicing of the botnet malware.
“Senakh and his co-conspirators utilised the Ebury botnet to generate and redirect internet visitors in furtherance of a variety of click-fraud and spam email schemes, which fraudulently generated hundreds of thousands of dollars in earnings,” the U.S. Justice Department claimed at the time.

“As aspect of his plea, Senakh admitted that he supported the criminal business by creating accounts with domain registrars that helped build the Ebury botnet infrastructure and individually profited from targeted visitors created by the Ebury botnet.”
ESET’s investigation has unearthed different approaches the attackers use to provide Ebury, such as strategies these kinds of as theft of SSH qualifications, credential stuffing, infiltrating hosting company infrastructure, exploitation of flaws in Management Web Panel (e.g., CVE-2021-45467), and SSH adversary-in-the-center (AitM) attacks.
The menace actors have also been observed applying faux or stolen identities to protect their tracks, not to mention compromising infrastructure employed by other perpetrators with the malware in order to satisfy their goals and confuse attribution attempts.
“An example is the compromise of servers responsible for accumulating data from Vidar Stealer,” ESET mentioned. “Ebury actors utilized the stolen identities attained via Vidar Stealer for renting server infrastructure and in their actions, sending legislation enforcement bodies in the wrong directions.”
In yet another instance, Ebury is mentioned to have been used to breach one of the Mirai botnet author’s methods and steal the code a lot before it was manufactured public.
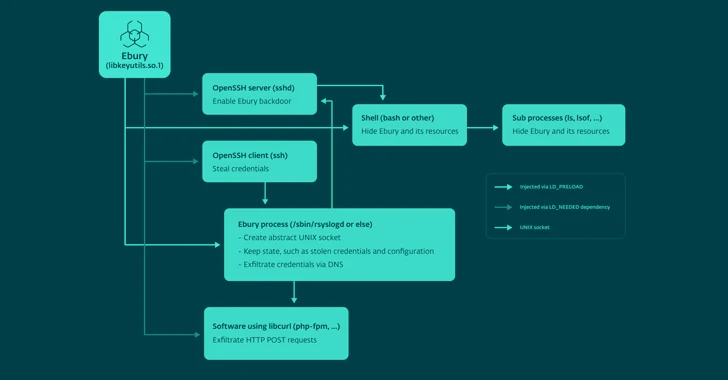
The malware also functions as a backdoor and SSH credential stealer, supplying attackers the capacity to deploy further payloads like HelimodSteal, HelimodProxy, and HelimodRedirect, and expand their existence in just a compromised network. The most up-to-date variation of Ebury known to date is 1.8.2.

“People tools have the common goal of monetizing, through numerous approaches, the servers they compromise,” ESET claimed. “The way servers are monetized variety from credit card information theft and cryptocurrency stealing to targeted traffic redirection, spam sending, and credential thieving.”
Although HelimodSteal, HelimodRedirect, and HelimodProxy are all HTTP server modules made use of for intercepting HTTP Publish requests made to the web server, redirect HTTP requests to adverts, and proxy targeted visitors to send out spam, the team also employs a kernel module identified as KernelRedirect that implements a Netfilter hook to modify HTTP site visitors to accomplish redirection.
Also utilized are software package to disguise and permit destructive website traffic through the firewall, as properly as Perl scripts to carry out substantial-scale AitM attacks in just hosting providers’ facts centers to breach useful targets and steal cryptocurrency from their wallets.
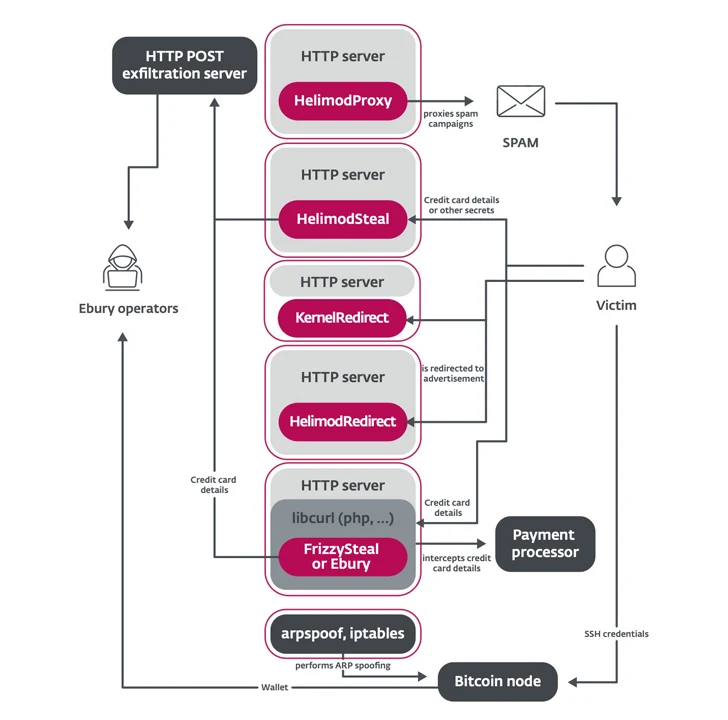
HelimodSteal is also made to seize credit score card facts that’s submitted by a victim to an online store, properly as a server-facet web skimmer to extract the information received by the contaminated server.
In an alternate chain of occasions, the monetary facts can be attained by usually means of Ebury or FrizzySteal, a malicious shared library that’s injected into libcurl and can exfiltrate requests made by the compromised server to exterior HTTP servers, these as a payment processor.
“Considering that both equally are functioning within just the web server or application, conclude-to-end encryption (HTTPS) cannot guard versus this threat,” ESET mentioned.
“Entry to servers applied for shared hosting grants them access to a good deal of unencrypted web targeted visitors, which they leverage for stealthy redirection or capturing information submitted in on the net kinds.”
Found this posting appealing? Stick to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read far more exceptional articles we submit.
Some parts of this short article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 It’s Time to Master the Lift & Shift: Migrating from VMware vSphere to Microsoft Azure
It’s Time to Master the Lift & Shift: Migrating from VMware vSphere to Microsoft Azure