Cybersecurity scientists have detailed an up to date variation of the malware HeadCrab which is acknowledged to focus on Redis databases servers across the environment considering the fact that early September 2021.
The growth, which comes exactly a calendar year soon after the malware was very first publicly disclosed by Aqua, is a indicator that the fiscally-motivated threat actor powering the campaign is actively adapting and refining their practices and tactics to stay ahead of the detection curve.
The cloud security business stated that “the marketing campaign has nearly doubled the variety of infected Redis servers,” with an additional 1,100 compromised servers, up from 1,200 claimed at the start out of 2023.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code

HeadCrab is created to infiltrate internet-exposed Redis servers and wrangle them into a botnet for illicitly mining cryptocurrency, although also leveraging the entry in a way that makes it possible for the risk actor to execute shell instructions, load fileless kernel modules, and exfiltrate info to a distant server.
Whilst the origins of the risk actor are presently not identified, they make it a place to note in a “mini weblog” embedded into the malware that the mining action is “legal in my place” and that they do it for the reason that “it practically will not damage human lifetime and emotions (if finished proper).”
The operator, nonetheless, acknowledges that it truly is a “parasitic and inefficient way” of making funds, adding their goal is to make $15,000 per yr.
“An integral factor of the sophistication of HeadCrab 2. lies in its advanced evasion strategies,” Aqua researchers Asaf Eitani and Nitzan Yaakov reported. “In distinction to its predecessor (named HeadCrab 1.), this new model employs a fileless loader system, demonstrating the attacker’s commitment to stealth and persistence.”
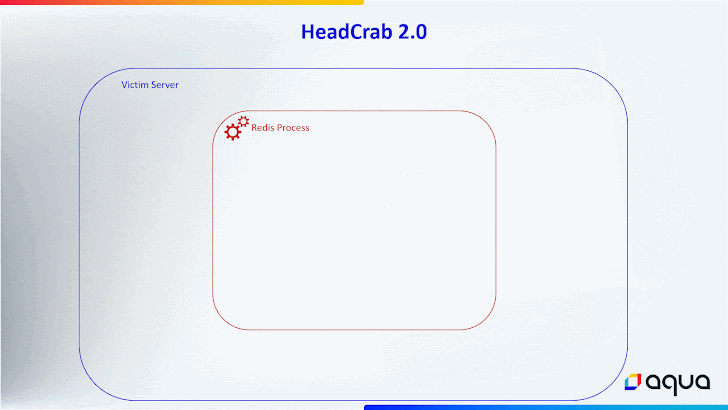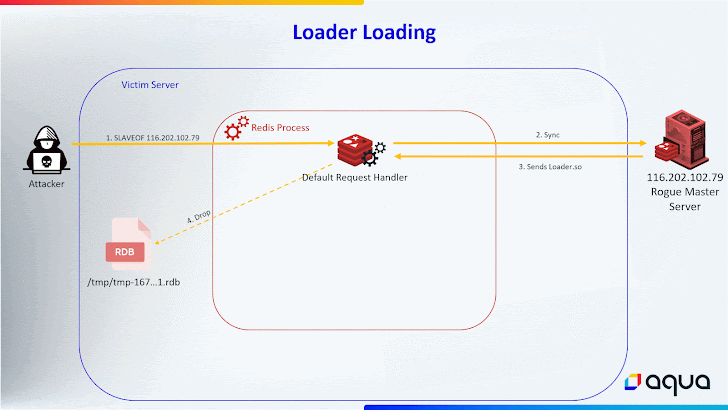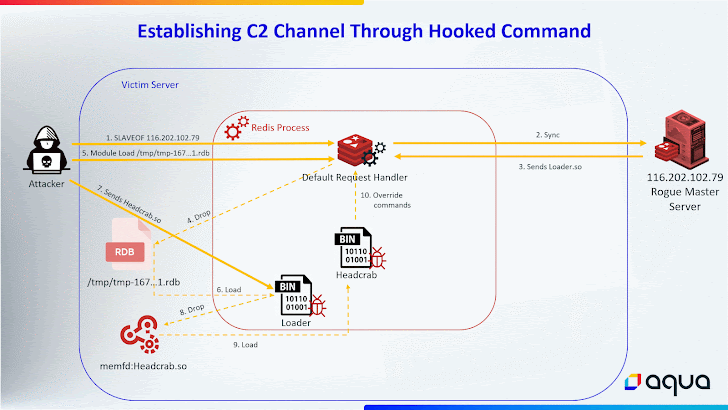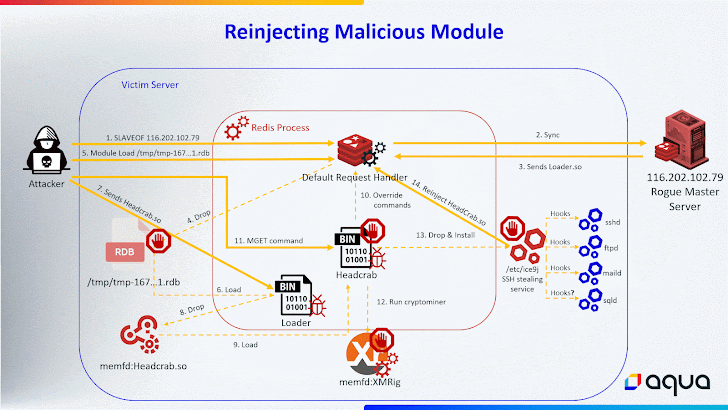
It is really really worth noting that the preceding iteration utilized the SLAVEOF command to down load and help save the HeadCrab malware file to disk, thus leaving artifact traces on the file procedure.
HeadCrab 2., on the other hand, receives the malware’s written content more than the Redis conversation channel and merchants it in a fileless area in a bid to lessen the forensic trail and make it significantly far more tough to detect.
Also transformed in the new variant is the use of the Redis MGET command for command-and-command (C2) communications for extra covertness.

“By hooking into this conventional command, the malware gains the capacity to regulate it through unique attacker-initiated requests,” the scientists explained.
“These requests are accomplished by sending a exclusive string as an argument to the MGET command. When this unique string is detected, the malware recognizes the command as originating from the attacker, triggering the destructive C2 conversation.”
Describing HeadCrab 2. as an escalation in the sophistication of Redis malware, Aqua mentioned its ability to masquerade its destructive actions less than the guise of authentic commands poses new complications for detection.
“This evolution underscores the requirement for continual investigation and improvement in security applications and tactics,” the researchers concluded. “The engagement by the attacker and the subsequent evolution of the malware highlights the critical have to have for vigilant checking and intelligence accumulating.”
Identified this report attention-grabbing? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read much more special articles we post.
Some components of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Warning: New Malware Emerges in Attacks Exploiting Ivanti VPN Vulnerabilities
Warning: New Malware Emerges in Attacks Exploiting Ivanti VPN Vulnerabilities