A new assessment of Raspberry Robin’s attack infrastructure has discovered that it is possible for other danger actors to repurpose the infections for their individual malicious actions, producing it an even a lot more potent threat.
Raspberry Robin (aka QNAP worm), attributed to a menace actor dubbed DEV-0856, is malware that has progressively appear underneath the radar for being used in attacks aimed at finance, authorities, insurance coverage, and telecom entities.
Specified its use numerous threat actors to fall a extensive vary of payloads these as SocGholish, Bumblebee, TrueBot, IcedID, and LockBit ransomware, it can be suspected to be a pay back-for every-install (PPI) botnet capable of serving upcoming-phase payloads.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
Raspberry Robin, notably, employs infected USB drives as a propagation system and leverages breached QNAP network-attached storage (NAS) products as very first-stage command-and-handle (C2).
Cybersecurity firm SEKOIA stated it was ready to recognize at least 8 digital private servers (VPSs) hosted on Linode that function as a 2nd C2 layer that probable act as forward proxies to the next as-still-not known tier.
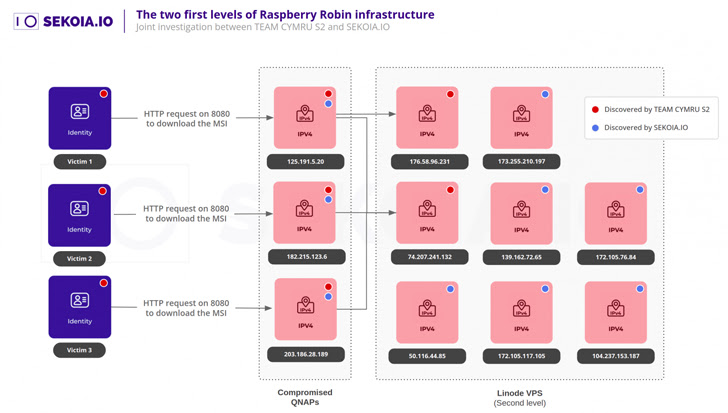
“Every single compromised QNAP would seem to act as a validator and forwarder,” the France-based corporation said. “If the gained request is legitimate, it is redirected to an upper degree of infrastructure.”
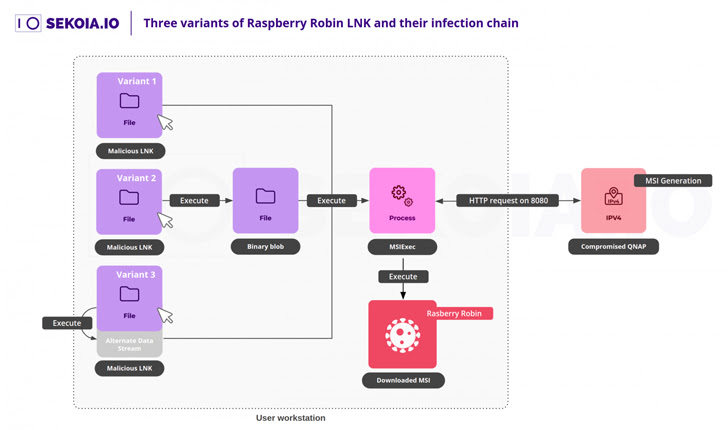
The attack chain as a result unfolds as follows: When a consumer inserts the USB drive and launches a Windows shortcut (.LNK) file, the msiexec utility is launched, which, in turn, downloads the primary obfuscated Raspberry Robin payload from the QNAP instance.
This reliance on msiexec to deliver out HTTP requests to fetch the malware will make it possible to hijack these requests to down load a further rogue MSI payload both by DNS hijacking attacks or paying for beforehand acknowledged domains immediately after their expiration.
One particular these types of area is tiua[.]uk, which was registered in the early days of the marketing campaign in late July 2021 and used as a C2 among September 22, 2021, and November 30, 2022, when it was suspended by the .UK registry.
“By pointing this area to our sinkhole, we had been able to acquire telemetry from just one of the very first domains applied by Raspberry Robin operators,” the company mentioned, incorporating it noticed many victims, indicating “it was still achievable to repurpose a Raspberry Robin area for malicious functions.”
The exact origins of how the initially wave of Raspberry Robin USB bacterial infections took position keep on being at the moment unfamiliar, despite the fact that it is suspected that it might have been reached by relying on other malware to disseminate the worm.
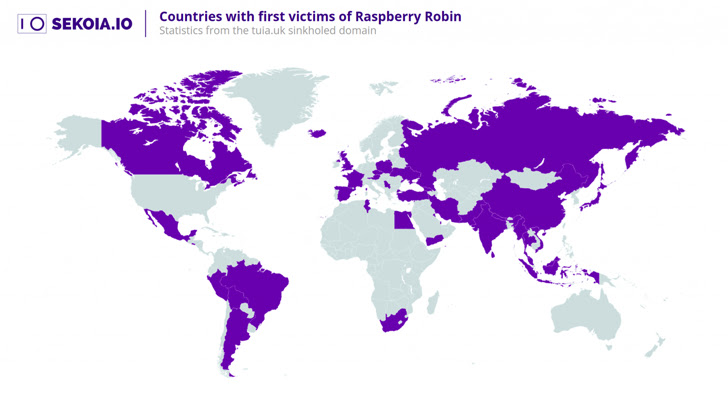
This hypothesis is evidenced by the presence of a .NET spreader module which is said to be accountable for distributing Raspberry Robin .LNK information from contaminated hosts to USB drives. These .LNK files subsequently compromise other equipment via the aforementioned system.
The development arrives days right after Google’s Mandiant disclosed that the Russia-connected Turla team reused expired domains involved with ANDROMEDA malware to deliver reconnaissance and backdoor applications to targets compromised by the latter in Ukraine.
“Botnets provide a number of purposes and can be reused and/or remodeled by their operators or even hijacked by other teams around time,” the researcher mentioned.
Uncovered this article fascinating? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read additional exclusive content we put up.
Some areas of this write-up are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Multiple Danish Banks Disrupted By DDoS Cyber-Attack
Multiple Danish Banks Disrupted By DDoS Cyber-Attack