Security scientists have uncovered however one more vulnerability impacting a lot of more mature AMD and Intel microprocessors that could bypass recent defenses and consequence in Spectre-dependent speculative-execution attacks.
Dubbed Retbleed by ETH Zurich researchers Johannes Wikner and Kaveh Razavi, the issue is tracked as CVE-2022-29900 (AMD) and CVE-2022-29901 (Intel), with the chipmakers releasing software program mitigations as part of a coordinated disclosure method.
Retbleed is also the latest addition to a course of Spectre attacks regarded as Spectre-BTI (CVE-2017-5715 or Spectre-V2), which exploit the facet consequences of an optimization system referred to as speculative execution by implies of a timing facet channel to trick a software into accessing arbitrary areas in its memory room and leak private info.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
Speculative execution tries to fill the instruction pipeline of a program by predicting which instruction will be executed future in buy to gain a performance improve, whilst also undoing the results of the execution ought to the guess transform out to be improper.
Attacks like Spectre take gain of the reality that these erroneously executed guidance — a consequence of the misprediction — are sure to go away traces of the execution in the cache, resulting in a scenario wherever a rogue program can trick the processor into executing incorrect code paths and infer secret data pertaining to the target.
Place in a different way, Spectre is an instance of transient execution attack, which depends on hardware design flaws to “influence” which instruction sequences are speculatively executed and leak encryption keys or passwords from inside the victim’s memory handle space.
This, in flip, is achieved via microarchitectural aspect channels like Flush+Reload that measures the time taken to execute memory reads from the cache that is shared with the target, but not ahead of flushing some of the shared memory, resulting in either quickly or sluggish reads dependent on no matter if the victim accessed the monitored cache line considering the fact that it was evicted.
While safeguards like Retpoline (aka “return trampoline”) have been devised to reduce department target injection (BTI), Retbleed is intended to get all around this countermeasure and accomplish speculative code execution.
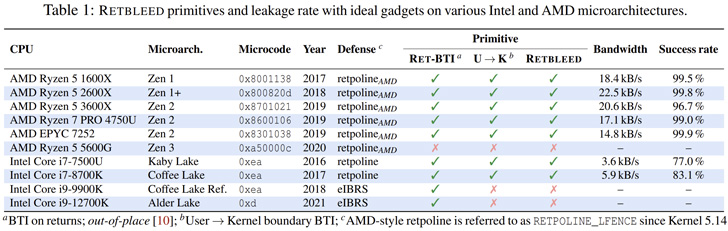
“Retpolines operate by changing oblique jumps [branches where the branch target is determined at runtime] and phone calls with returns,” the researchers spelled out.
“Retbleed aims to hijack a return instruction in the kernel to get arbitrary speculative code execution in the kernel context. With sufficient handle over registers and/or memory at the target return instruction, the attacker can leak arbitrary kernel knowledge.”

The main strategy, in a nutshell, is to deal with return recommendations as an attack vector for speculation execution and force the statements to be predicted like oblique branches, successfully undoing protections offered by Retpoline.
As a new line of defense, AMD has launched what is actually referred to as Jmp2Ret, even though Intel has suggested making use of enhanced Oblique Branch Limited Speculation (eIBRS) to deal with the probable vulnerability even if Retpoline mitigations are in location.
“Windows running program utilizes IBRS by default, so no update is needed,” Intel mentioned in an advisory, noting it labored with the Linux group to make available software program updates for the shortcoming.
Identified this write-up appealing? Abide by THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to examine more unique articles we article.
Some parts of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 U.S. FTC Vows to Crack Down on illegal Use and Sharing of Citizens’ Sensitive Data
U.S. FTC Vows to Crack Down on illegal Use and Sharing of Citizens’ Sensitive Data