A new research has recognized four new variants of HTTP ask for smuggling assaults that get the job done towards many professional off-the-shelf web servers and HTTP proxy servers.
Amit Klein, VP of Security Exploration at SafeBreach who introduced the results nowadays at the Black Hat security convention, explained that the assaults highlight how web servers and HTTP proxy servers are however susceptible to HTTP request smuggling even just after 15 decades due to the fact they had been very first documented.
What is HTTP Request Smuggling?
HTTP request smuggling (or HTTP Desyncing) is a system employed to interfere with the way a website procedures sequences of HTTP requests that are received from one particular or a lot more users.
Vulnerabilities relevant to HTTP request smuggling normally arise when the front-stop (a load balancer or proxy) and the back-conclusion servers interpret the boundary of an HTTP ask for in a different way, therefore making it possible for a lousy actor to ship (or “smuggle”) an ambiguous request that will get prepended to the subsequent genuine user request.
This desynchronization of requests can be exploited to hijack credentials, inject responses to consumers, and even steal facts from a victim’s ask for and exfiltrate the details to an attacker-managed server.
The system was initial shown in 2005 by a group of researchers from Watchfire, like Klein, Chaim Linhart, Ronen Heled, and Steve Orrin. But in the very last 5 several years, a number of advancements have been devised, substantially expanding on the attack surface to splice requests into other individuals and “gain optimum privilege entry to interior APIs,” poison web caches, and compromise login internet pages of common applications.
What’s New?
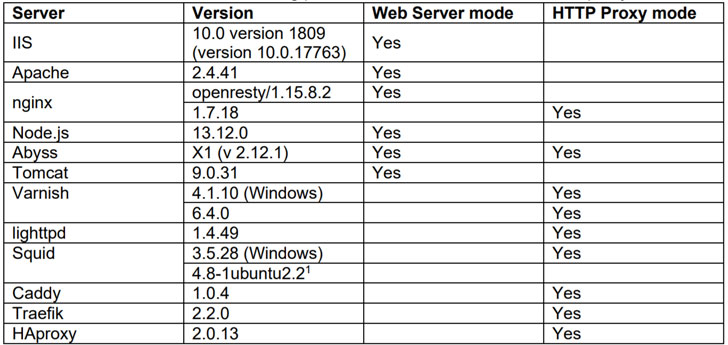
The new variants disclosed by Klein involve using many proxy-server combinations, such as Aprelium’s Abyss, Microsoft IIS, Apache, and Tomcat in the web-server method, and Nginx, Squid, HAProxy, Caddy, and Traefik in the HTTP proxy method.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
The list of all new four new variants is as below, together with an outdated one particular that the researcher correctly exploited in his experiments.
- Variant 1: “Header SP/CR junk: …”
- Variant 2 – “Wait around for It”
- Variant 3 – HTTP/1.2 to bypass mod_security-like protection
- Variant 4 – a simple solution
- Variant 5 – “CR header”
When dealing with HTTP requests containing two Information-Size header fields, Abyss, for example, was located to settle for the 2nd header as valid, whereas Squid used the first Information-Size header, therefore top the two servers to interpret the requests otherwise and obtain request smuggling.
In predicaments in which Abyss will get an HTTP ask for with a body whose length is considerably less than the specified Written content-Duration worth, it waits for 30 seconds to fulfill the ask for, but not prior to ignoring the remaining human body of the request. Klein located that this also results in discrepancies in between Squid and Abyss, with the latter deciphering portions of the outbound HTTP ask for as a second request.
A 3rd variant of the attack works by using HTTP/1.2 to circumvent WAF defenses as outlined in OWASP ModSecurity Main Rule Set (CRS) for protecting against HTTP request smuggling attacks craft a malicious payload that triggers the behavior.
Last of all, Klein discovered that working with the “Content-Form: textual content/basic” header discipline was enough to bypass paranoia level checks 1 and 2 specified in CRS and generate an HTTP Request Smuggling vulnerability.
What Are the Feasible Defenses?
Immediately after the results were disclosed to Aprelium, Squid, and OWASP CRS, the issues were being mounted in Abyss X1 v2.14, Squid versions 4.12, and 5..3 and CRS v3.3..
Contacting for normalization of outbound HTTP Requests from proxy servers, Klein pressured the need for an open source, robust web application firewall option that’s capable of handling HTTP Request Smuggling attacks.
“ModSecurity (put together with CRS) is certainly an open up source undertaking, but as for robustness and genericity, mod_security has quite a few disadvantages,” Klein noted. “It does not provide total security against HTTP Ask for Smuggling [and] it is only obtainable for Apache, IIS and nginx.”
To this close, Klein has printed a C++-dependent library that assures that all incoming HTTP requests are totally valid, compliant, and unambiguous by implementing stringent adherence to HTTP header format and request line format. It can be accessed from GitHub here.
Located this post interesting? Stick to THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to study additional exceptional information we post.


 Scientists Name Condition with Fewest Info Breaches
Scientists Name Condition with Fewest Info Breaches