Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered an “implementation vulnerability” that has designed it probable to reconstruct encryption keys and decrypt data locked by Rhysida ransomware.
The results were being published final week by a group of researchers from Kookmin University and the Korea Internet and Security Company (KISA).
“By means of a comprehensive analysis of Rhysida Ransomware, we recognized an implementation vulnerability, enabling us to regenerate the encryption critical employed by the malware,” the scientists said.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
The enhancement marks the very first successful decryption of the ransomware pressure, which to start with built its physical appearance in May perhaps 2023. A restoration resource is becoming distributed through KISA.

The research is also the latest to attain details decryption by exploiting implementation vulnerabilities in ransomware, right after Magniber v2, Ragnar Locker, Avaddon, and Hive.
Rhysida, which is recognized to share overlaps with an additional ransomware crew known as Vice Society, leverages a tactic identified as double extortion to apply force on victims into paying out up by threatening to launch their stolen information.
An advisory posted by the U.S. government in November 2023 termed out the risk actors for staging opportunistic attacks targeting education and learning, production, facts technology, and federal government sectors.
A complete evaluation of the ransomware’s internal workings has revealed its use of LibTomCrypt for encryption as effectively as parallel processing to pace up the approach. It has also been found to put into action intermittent encryption (aka partial encryption) to evade detection by security remedies.
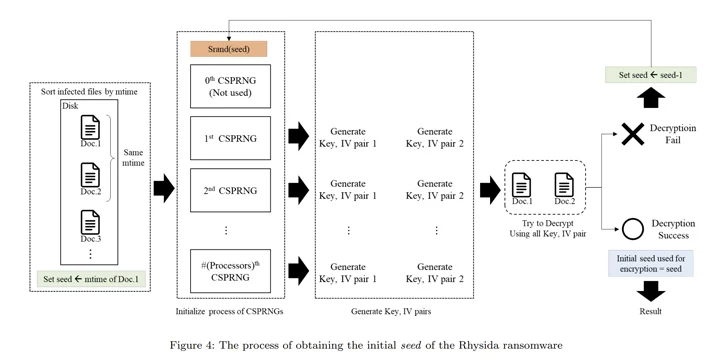
“Rhysida ransomware utilizes a cryptographically protected pseudo-random amount generator (CSPRNG) to make the encryption crucial,” the researchers said. “This generator takes advantage of a cryptographically secure algorithm to produce random figures.”
Specifically, the CSPRNG is based mostly on the ChaCha20 algorithm supplied by the LibTomCrypt library, with the random variety produced also correlated to the time at which Rhysida ransomware is working.

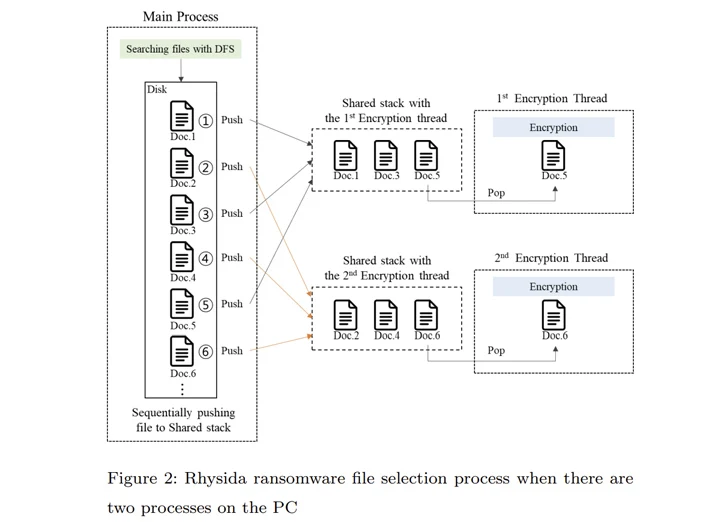
That’s not all. The principal procedure of Rhysida ransomware compiles a checklist of files to be encrypted. This listing is subsequently referenced by several threads established to at the same time encrypt the documents in a specific get.
“In the encryption method of the Rhysida ransomware, the encryption thread generates 80 bytes of random numbers when encrypting a single file,” the researchers noted. “Of these, the 1st 48 bytes are employed as the encryption important and the [initialization vector].”
Making use of these observations as reference points, the researchers explained they were being in a position to retrieve the preliminary seed for decrypting the ransomware, figure out the “randomized” purchase in which the files were being encrypted, and in the end recuperate the facts without having possessing to fork out a ransom.
“Despite the fact that these research have a restricted scope, it is crucial to admit that sure ransomwares […] can be properly decrypted,” the scientists concluded.
Observed this write-up appealing? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to browse more distinctive written content we post.
Some pieces of this short article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 4 Ways Hackers use Social Engineering to Bypass MFA
4 Ways Hackers use Social Engineering to Bypass MFA