Cybersecurity researchers have taken the wraps off what they phone a “nearly-difficult-to-detect” Linux malware that could be weaponized to backdoor contaminated techniques.
Dubbed Symbiote by menace intelligence corporations BlackBerry and Intezer, the stealthy malware is so named for its potential to conceal alone inside of functioning procedures and network site visitors and drain a victim’s sources like a parasite.
The operators powering Symbiote are thought to have commenced enhancement on the malware in November 2021, with the risk actor predominantly working with it to goal the financial sector in Latin The usa, including financial institutions like Banco do Brasil and Caixa.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
“Symbiote’s principal objective is to capture qualifications and to facilitate backdoor entry to a victim’s equipment,” researchers Joakim Kennedy and Ismael Valenzuela explained in a report shared with The Hacker Information. “What helps make Symbiote distinctive from other Linux malware is that it infects jogging processes rather than making use of a standalone executable file to inflict destruction.”

It achieves this by leveraging a native Linux element named LD_PRELOAD — a system formerly employed by malware such as Pro-Ocean and Facefish — so as to be loaded by the dynamic linker into all running procedures and infect the host.
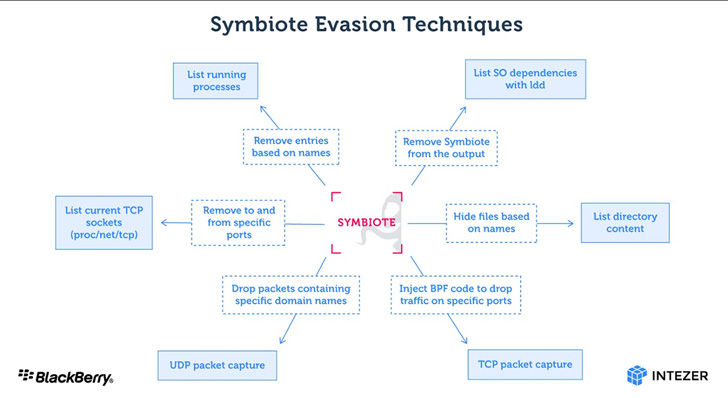
Moreover hiding its existence on the file method, Symbiote is also capable of cloaking its network targeted traffic by building use of the prolonged Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) aspect. This is carried out by injecting alone into an inspection software’s procedure and using BPF to filter out final results that would uncover its exercise.
On hijacking all functioning procedures, Symbiote enables rootkit functionality to further conceal proof of its presence and supplies a backdoor for the risk actor to log in to the machine and execute privileged instructions. It has also been observed storing captured credentials encrypted in documents masquerading as C header data files.

This is not the first time a malware with similar abilities has been spotted in the wild. In February 2014, ESET uncovered a Linux backdoor known as Ebury which is built to steal OpenSSH credentials and manage obtain to a compromised server.
“Considering the fact that the malware operates as a person-land degree rootkit, detecting an an infection might be tough,” the researchers concluded. “Network telemetry can be applied to detect anomalous DNS requests and security applications such as AVs and EDRs should be statically connected to ensure they are not ‘infected’ by userland rootkits.”
Identified this report appealing? Stick to THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to go through much more distinctive information we post.
Some areas of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Even the Most Advanced Threats Rely on Unpatched Systems
Even the Most Advanced Threats Rely on Unpatched Systems