Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed specifics of a now-patched zero-day flaw in Google Cloud System (GCP) that could have enabled risk actors to conceal an unremovable, malicious software within a victim’s Google account.
Israeli cybersecurity startup Astrix Security, which discovered and documented the issue to Google on June 19, 2022, dubbed the shortcoming GhostToken.
The issue impacted all Google accounts, like organization-centered Workspace accounts. Google deployed a international-patch much more than nine months afterwards on April 7, 2023.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
“The vulnerability […] will allow attackers to achieve permanent and unremovable access to a victim’s Google account by changing an now approved 3rd-party application into a malicious trojan app, leaving the victim’s personal facts uncovered eternally,” Astrix stated in a report.
In a nutshell, the flaw would make it doable for an attacker to hide their malicious app from a victim’s Google account software management site, thus successfully avoiding end users from revoking its obtain.
This is achieved by deleting the GCP job associated with the authorized OAuth application, leading to it to go in a “pending deletion” state. The menace actor, armed with this functionality, could then unhide the rogue application by restoring the undertaking and use the accessibility token to get hold of the victim’s knowledge, and make it invisible all over again.
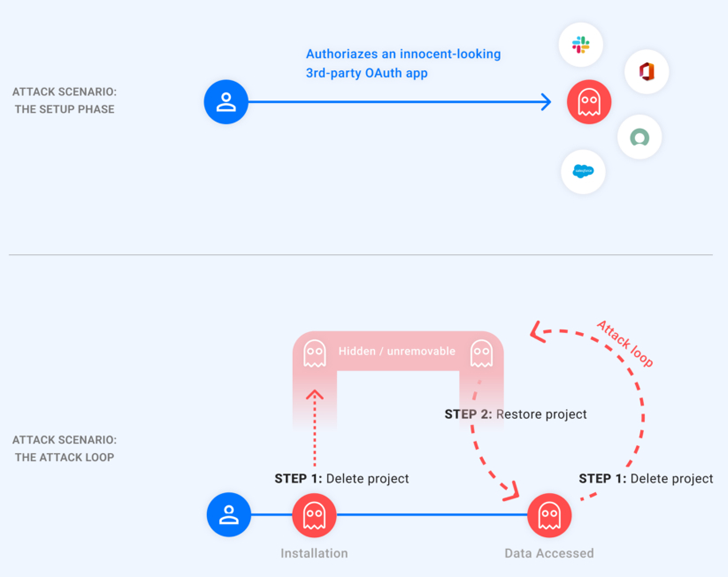
“In other words, the attacker holds a ‘ghost’ token to the victim’s account,” Astrix reported.
The type of info that can be accessed is dependent on the permissions granted to the application, which the adversaries can abuse to delete documents from Google Drive, produce email messages on the victim’s behalf to accomplish social engineering attacks, track locations, and exfiltrate sensitive data from Google Calendar, Images, and Push.
“Victims may unknowingly authorize obtain to such destructive apps by setting up a seemingly innocent application from the Google Market or one particular of the many productivity tools accessible on line,” Astrix included.
Approaching WEBINARZero Trust + Deception: Find out How to Outsmart Attackers!
Learn how Deception can detect advanced threats, prevent lateral movement, and increase your Zero Believe in tactic. Be part of our insightful webinar!
Help you save My Seat!
“As soon as the destructive app has been authorized, an attacker exploiting the vulnerability can bypass Google’s “Applications with obtain to your account” administration attribute, which is the only position wherever Google consumers can look at 3rd-party applications related to their account.”
Google’s patch addresses the challenge by now exhibiting apps that are in a pending deletion state on the third-party entry webpage, making it possible for end users to revoke the authorization granted to these kinds of applications.
The findings arrive a tiny about a month immediately after cloud incident reaction firm Mitiga uncovered that adversaries could acquire gain of “inadequate” forensic visibility into GCP to exfiltrate sensitive info.
Located this short article attention-grabbing? Stick to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read a lot more unique information we publish.
Some sections of this report are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 14 Kubernetes and Cloud Security Challenges and How to Solve Them
14 Kubernetes and Cloud Security Challenges and How to Solve Them