Attackers are increasingly earning use of “networkless” attack techniques targeting cloud applications and identities. Here’s how attackers can (and are) compromising businesses – without ever needing to touch the endpoint or standard networked methods and services.
Right before acquiring into the facts of the attack approaches becoming employed, let’s focus on why these attacks are getting additional commonplace.
SaaS adoption is switching the make-up of organization IT
The SaaS revolution and merchandise-led progress have experienced a large impact on the construction of organization networks, and where by core business enterprise programs and information reside.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
Most companies nowadays are working with tens to hundreds of SaaS programs throughout company capabilities. Some are solely SaaS-indigenous, with no conventional network to converse of, but most have adopted a hybrid design with a combination of on-premise, cloud, and SaaS products and services forming the spine of enterprise purposes becoming made use of.
The bulk of SaaS adoption is consumer-pushed, as opposed to centrally managed by IT, as bottom-up adoption is inherent to product or service-led advancement. The most recent data from Push Security suggests that only 1 in 5 SaaS apps have been sanctioned by the company. The vast majority is simply unidentified and, therefore, has not been reviewed at all.
Cloud and SaaS applications are developed to be interconnected, performing like the shut networks of interior organization apps you could possibly have utilized in the earlier. The car for this interconnectedness is identity.
Electronic identities are ever more intricate and challenging to secure
The most simple sort of identification is a person account designed for solutions you indication up to with a username/email and password. To cut down the risk of account takeover and complexity of running an ever-raising number of accounts, companies are working with the providers of identification suppliers (IdPs) to centralize obtain to apps inside of a single system and identity, applying protocols like single indicator on (SSO) and OAuth to deal with authentication and authorization respectively.
The individual make-up of an identity can vary a lot. Relying on the app, it is attainable to have multiple authentication mechanisms for the similar account – for case in point, by means of SAML, social logins (OIDC), and username and password. Whilst SAML demands that admins set it up in advance for a provided application tenant, customers can indication up for an app using OIDC just by working with the “indication in with Google” characteristic.
In result this results in several identities tied to a one account, which can introduce a ton of confusion and complexity – for illustration, just since an IdP admin deletes that account, will not signify the application/account are not able to then be accessed by utilizing 1 of the other login strategies that is been designed. This can make it tough to know what apps are in use, and what identities exist in the organization.
So, in follow, it’s achievable to close up with a blend of the next:
- Identification companies (normally 3 for each group on ordinary) (e.g., Okta, Entra/Microsoft, Google)
- Applications performing as an SSO platform for linked apps (e.g., Atlassian Accessibility, Adobe Creative Cloud)
- SaaS applications utilizing various authentication (SAML, OIDC) and authorization (OAuth) protocols
- SaaS applications with a community username and password
- Credentials and secrets and techniques stored in password manager and authenticator applications (which can be in browsers, on regional OS, and in 3rd party apps)
It can get pretty difficult – with most businesses obtaining 100+ apps in their inventory, ensuing in hundreds of sprawled identities.
Then, relying on the OAuth scopes authorized for a given application, permissions and workflows in one particular application can impact other applications exactly where acceptance is granted for them to speak to a single one more.
Identification is the glue that holds this ecosystem together. However, the controls that exist to safe identity have major constraints. Companies normally think that all their applications and identities have MFA rolled out or all apps are behind SSO. But the fact is that only 1/3 of apps really guidance SSO (and quite a few of these only at the high quality tier, with a significant price tag improve). More, all over 60% of one of a kind identities (i.e., not employing SSO) do not have MFA registered.
So in reality, there are substantial gaps in the security controls shielding cloud identities, whilst identities and cloud apps are turning out to be much more commonplace.
Attackers are targeting cloud identification vulnerabilities
Attackers are getting notice of this. In accordance to Verizon’s 2024 DBIR, 74% of all breaches involved the human factor, targeting compromised person accounts by using human error, privilege misuse, use of compromised credentials, or social engineering.
Although this is nothing at all new (some description of identity/phishing attacks have been the top rated attack vector due to the fact at minimum 2013), Crowdstrike’s newest worldwide risk report goes additional, noting that 75% of attacks to gain accessibility were being malware-totally free, and that “cloud-conscious” attacks (deliberate relatively than opportunistic focusing on of cloud products and services to compromise particular performance) increased 110%. Microsoft also notes around 4,000 password attacks for every next specially targeting cloud identities, although there are recommendations from Google workers that attacks on the lookout to steal session cookies (and hence bypass MFA) occur at around the exact purchase of magnitude as password-primarily based attacks.
Seeking further than the numbers, evidence from breaches in the community eye tells the same tale. Risk groups like APT29/Cozy Bear/The Dukes and Scattered Spider/0ktapus exhibit how attackers are actively targeting IdP companies, SaaS apps, and SSO/OAuth to have out superior-profile attacks versus companies like Microsoft and Okta.
If you want to go through more about this, you can look at out this web site write-up tracking identification attacks witnessed in the wild.
Cloud applications and identities are the new land of possibility for attackers. For the reason that of the shift to cloud companies, they give the identical price as a standard attack designed to breach a network perimeter through the endpoint. In many methods, id by itself is the new attack surface. Contrary to other security boundaries like the network or endpoint, it also provides substantially significantly less of an impediment in conditions of the controls that at the moment exist to defend this new perimeter.
Id-dependent attacks utilised to be localized to the endpoint or adjacent “identity systems” like Lively Listing. The goal for the attacker was to breach this perimeter and shift inside the organization. Now, id is much much more dispersed – the gateway to an ecosystem of interconnected cloud apps and expert services, all accessed over the internet. This has noticeably shifted the magnitude of the obstacle going through security teams. Right after all, it really is significantly tougher to halt credential-stuffing attacks in opposition to 100 SaaS applications than the solitary centralized exterior VPN/webmail endpoint of yesteryear.
Cloud identities are the new perimeter
It seems very very clear that cloud identities are the new electronic perimeter. This just isn’t the foreseeable future, it can be now. The only piece that is nonetheless to be decided is what offensive approaches and tradecraft will arise, and what the sector reaction will be in get to stop them.
Security period Approaches of the day Industry response 2000s Conventional perimeter hacking Port scanners, vuln scanners, buffer overflows, web application attacks, WiFi hacking, shopper/server backdoors Firewalls, DMZs, patch administration, secure coding, WPA, penetration screening 2010s Endpoint is the new perimeter Phishing, business macros, file format bugs, browser exploits, memory resident implants, C2 frameworks Endpoint hardening, EDR, SIEMS, purple teaming, menace hunting 2020s Cloud identities are the new perimeter ??? ???
Previous 12 months, Push Security produced a matrix of SaaS attack approaches on GitHub (inspired by the far more endpoint-concentrated MITRE ATT&CK Framework) that demonstrates how attackers can focus on a business enterprise without having touching classic surfaces these as the network or endpoints.
When chained alongside one another, these methods permit an attacker to total an conclusion-to-close attack in the cloud.
Force has also unveiled a number of website posts covering how these tactics can be utilised – the most well-known procedures are summarized under:
TechniqueOverviewAiTM phishingAiTM phishing works by using dedicated tooling to act as a web proxy between the sufferer and a respectable login portal for an software the sufferer has entry to, principally to make it less complicated to defeat MFA protection. By proxying in real-time to the goal login portal, the adversary is given entry to both equally a valid password and valid session cookies they can steal and use to hijack the session. As soon as logged-in, a sufferer person will see all the authentic details they would count on to see ordinarily (e.g. their personal email messages/information and many others) as it is a proxy of the real application. This reduces their chances of realizing they have been compromised owing to the authentic working mother nature of the proxied application.IM phishingIM apps like Groups and Slack are a terrific way for attackers to evade additional stringent email-dependent phishing protections all over destructive inbound links and attachments. The immediacy and true-time nature of IM will make it a handy vector for phishing attacks as people are considerably less familiar with these applications as supply vectors for phishing attacks. Applying IM, it is achievable to spoof/impersonate consumers, use bot accounts to generate believable dialogue, abuse hyperlink preview performance, and retrospectively edit messages and accounts to clear up your tracks.SAMLjackingSAMLjacking is wherever an attacker can make use of SAML SSO configuration configurations for a SaaS tenant they regulate in order to redirect consumers to a malicious hyperlink of their deciding on all through the authentication procedure. This can be highly effective for phishing as the authentic URL will be a reputable SaaS URL and users are anticipating to present qualifications. It can also be made use of for lateral motion if an admin account for a SaaS application is compromised, by modifying or enabling SAML, pointing the URL to a credential phishing website page that seems like or proxies a legit authentication assistance (e.g. Google or Microsoft). The adversary can then concentrate on customers by sending seemingly genuine one-way links to the app login page to the tenant, which then functions in the way of a watering gap attack.OktajackingAn attacker can set-up their individual Okta tenant to be applied in very convincing phishing attacks. This attack works for the reason that Okta forwards credentials from logins for accounts tied to Ad to its own Ad agent that operates on the goal network. Then, Okta enables the agent to report back again to them about no matter whether the login really should be prosperous or not. This permits an attacker who has compromised an Advertisement agent, or is ready to emulate a single, to equally keep track of login qualifications for Okta people and deliver skeleton important-like features to authenticate to Okta as any consumer they like. It can also be used similarly to SAMLjacking for lateral movement – other than you do not need to have to redirect to a individual malicious area.Shadow workflowsA shadow workflow is a method for making use of SaaS automation apps to supply a code execution-like approach for conducting destructive actions from a legitimate resource working with OAuth integrations. This could be a daily export of documents from shared cloud drives, automated forwarding and deleting of e-mail, cloning prompt messages, exporting consumer directories — in essence something that is attainable employing the focus on app’s API.
Networkless attack techniques in action
But there is certainly absolutely nothing quite like observing them in action to recognize just how impactful these methods can be. So look at out the clip under from Luke Jennings, VP of R&D at Press. In this movie, he covers:
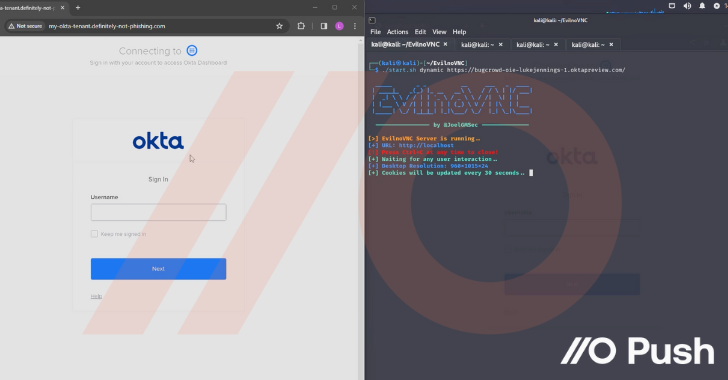
- Preliminary entry by using AiTM phishing making use of EvilNoVNC, a Browser in the Browser (BitB) phishing framework, to hijack a person Okta session
- Stealing credentials from the browser session and accessing additional applications by using Okta SSO, configuring these apps to make persistent obtain and backdoor the apps
- Accomplishing more credential theft for other end users of people apps inside of the corporate tenant by abusing SAML and SWA logins
- Directly accessing sensitive facts and features in compromised applications
Could you detect and respond to this attack?
Soon after seeing what is actually probable, it really is significant to talk to – could you detect and respond to this attack state of affairs?
- Would you detect the preliminary AiTM phish?
- How a lot of customers would be compromised by way of the SAMLjacking attack?
- Would you locate all the distinct backdoors in a number of SaaS applications?
- …or just reset the password and MFA tokens for the Okta account?
- …and what about the passwords for all the non-SAML applications?
Most organizations have a security gap when it comes to identification-centered attacks. This is in significant part for the reason that the controls close to identity security are ordinarily concentrated on securing central id methods (believe Lively Listing/Entra ID) as opposed to the larger identification infrastructure as it relates to cloud apps and expert services.
Similarly, the controls that businesses have invested in are largely bypassed by these attacks. EDR tools applied to safe underlying operating units have minimal existence here simply because these applications are accessed in the browser – ever more touted as the new functioning technique. As reviewed in this article, securing the identity is definitely essential to guarding companies in the cloud. And a sizeable part of the attack chain – for example, phishing attempts in typical, like AiTM and BitB methods developed to bypass MFA, or password sharing throughout apps and products and services, are merely not protected by endpoint security tools, IdP logs, or SaaS logs from particular person applications and companies.
These forms of attacks are a authentic problem for lots of businesses proper now for the reason that they fall via the cracks of existing security tools and companies.
Fascinated in discovering much more?
If you want to uncover out much more about identification attacks in the cloud and how to stop them, check out out Press Security – you can check out out their browser-dependent agent for free of charge!
Observed this report interesting? This posting is a contributed piece from one particular of our valued associates. Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study additional exceptional content we post.
Some sections of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Akira Ransomware Gang Extorts $42 Million; Now Targets Linux Servers
Akira Ransomware Gang Extorts $42 Million; Now Targets Linux Servers