Two new security weaknesses discovered in various electric motor vehicle (EV) charging methods could be exploited to remotely shut down charging stations and even expose them to data and strength theft.
The conclusions, which appear from Israel-based mostly SaiFlow, the moment once again display the opportunity dangers going through the EV charging infrastructure.
The issues have been identified in edition 1.6J of the Open Charge Level Protocol (OCPP) typical that works by using WebSockets for interaction among EV charging stations and the Charging Station Administration Program (CSMS) companies. The latest version of OCPP is 2..1.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
“The OCPP common would not define how a CSMS must accept new connections from a charge stage when there is currently an energetic connection,” SaiFlow scientists Lionel Richard Saposnik and Doron Porat said.
“The absence of a crystal clear guideline for a number of active connections can be exploited by attackers to disrupt and hijack the link in between the demand position and the CSMS.”
This also indicates that a cyber attacker could spoof a connection from a legitimate charger to its CSMS supplier when it is by now related, efficiently top to possibly of the two situations:
- A denial-of-services (DoS) problem that arises when the CSMS service provider closes the original the WebSocket link when a new relationship is proven
- Information and facts theft that stems from maintaining the two connections alive but returning responses to the “new” rogue link, permitting the adversary to obtain the driver’s personal facts, credit card information, and CSMS qualifications.
The forging is designed attainable owing to the point that CSMS vendors are configured to solely depend on the charging issue identification for authentication.
“Combining the mishandling of new connections with the weak OCPP authentication and chargers identities policy could direct to a large Dispersed DoS (DDoS) attack on the [Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment] network,” the researchers mentioned.
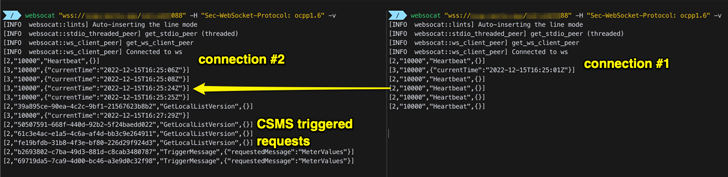
OCPP 2..1 remediates the weak authentication coverage by demanding charging issue credentials, therefore closing out the loophole. That explained, mitigations for when there are a lot more than a single link from a solitary charging place should really necessitate validating the connections by sending a ping or a heartbeat ask for, SaiFlow noted.
“If one particular of the connections is not responsive, the CSMS should really reduce it,” the researchers defined. “If both connections are responsive, the operator really should be ready to do away with the malicious connection straight or by means of a CSMS-built-in cybersecurity module.”
Located this write-up attention-grabbing? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read through more exceptional material we post.
Some elements of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Post-Macro World Sees Rise in Microsoft OneNote Documents Delivering Malware
Post-Macro World Sees Rise in Microsoft OneNote Documents Delivering Malware