Various security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the TCP/IP network protocol stack of an open-resource reference implementation of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specification used extensively in modern day computers.
Collectively dubbed PixieFail by Quarkslab, the nine issues reside in the TianoCore EFI Improvement Package II (EDK II) and could be exploited to realize remote code execution, denial-of-assistance (DoS), DNS cache poisoning, and leakage of delicate information and facts.
UEFI firmware – which is accountable for booting the functioning process – from AMI, Intel, Insyde, and Phoenix Systems are impacted by the shortcomings.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
EDK II incorporates its personal TCP/IP stack referred to as NetworkPkg to permit network functionalities accessible throughout the first Preboot eXecution Atmosphere (PXE, pronounced “pixie”) phase, which allows for management duties in the absence of a jogging working program.

In other terms, it is a shopper-server interface to boot a unit from its network interface card (NIC) and enables networked computer systems that are not still loaded with an functioning program to be configured and booted remotely by an administrator.
The code to PXE is incorporated as section of the UEFI firmware on the motherboard or within the NIC firmware go through-only memory (ROM).
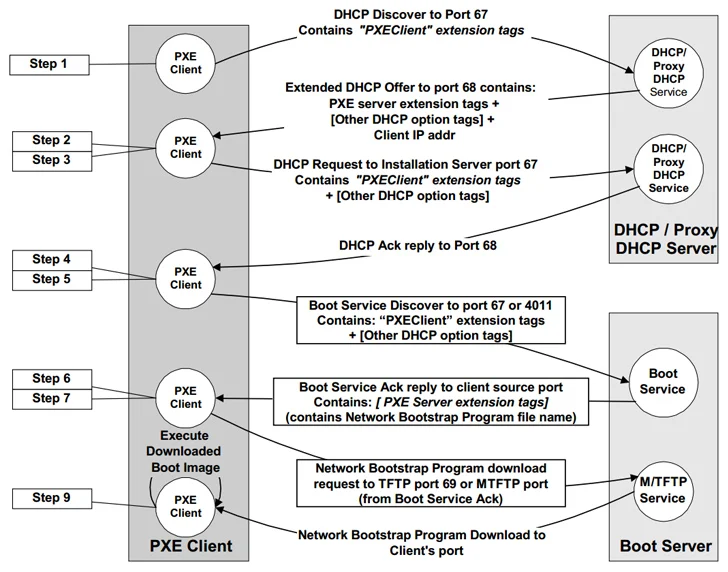
The issues determined by Quarkslab within just the EDKII’s NetworkPkg encompass overflow bugs, out-of-bounds study, infinite loops, and the use of weak pseudorandom quantity generator (PRNG) that consequence in DNS and DHCP poisoning attacks, information and facts leakage, denial of service, and info insertion attacks at the IPv4 and IPv6 layer.
The record of flaws is as follows –
- CVE-2023-45229 (CVSS score: 6.5) – Integer underflow when processing IA_NA/IA_TA choices in a DHCPv6 Promote message
- CVE-2023-45230 (CVSS rating: 8.3) – Buffer overflow in the DHCPv6 customer by using a extended Server ID alternative
- CVE-2023-45231 (CVSS rating: 6.5) – Out-of-bounds go through when dealing with a ND Redirect information with truncated selections
- CVE-2023-45232 (CVSS rating: 7.5) – Infinite loop when parsing unknown possibilities in the Place Selections header
- CVE-2023-45233 (CVSS score: 7.5) – Infinite loop when parsing a PadN option in the Destination Solutions header
- CVE-2023-45234 (CVSS score: 8.3) – Buffer overflow when processing DNS Servers choice in a DHCPv6 Promote information
- CVE-2023-45235 (CVSS rating: 8.3) – Buffer overflow when dealing with Server ID possibility from a DHCPv6 proxy Market message
- CVE-2023-45236 (CVSS score: 5.8) – Predictable TCP Preliminary Sequence Figures
- CVE-2023-45237 (CVSS score: 5.3) – Use of a weak pseudorandom amount generator

“The effects and exploitability of these vulnerabilities rely on the certain firmware establish and the default PXE boot configuration,” the CERT Coordination Heart (CERT/CC) stated in an advisory.
“An attacker in the area network (and, in certain eventualities remotely) could exploit these weaknesses to execute distant code, initiate DoS attacks, carry out DNS cache poisoning, or extract delicate info.”
Discovered this posting fascinating? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read a lot more distinctive content material we article.
Some components of this write-up are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 Iranian Hackers Masquerades as Journalists to Spy on Israel-Hamas War Experts
Iranian Hackers Masquerades as Journalists to Spy on Israel-Hamas War Experts