A number of security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the Intelligent Platform Administration Interface (IPMI) firmware for Supermicro baseboard management controllers (BMCs) that could outcome in privilege escalation and execution of malicious code on afflicted units.
The seven flaws, tracked from CVE-2023-40284 through CVE-2023-40290, fluctuate in severity from High to Critical, according to Binarly, enabling unauthenticated actors to obtain root entry to the BMC technique. Supermicro has transported a BMC firmware update to patch the bugs.
BMCs are specific processors on server motherboards that assistance distant administration, enabling administrators to keep an eye on hardware indicators these types of as temperature, established admirer velocity, and update the UEFI system firmware. What is more, BMC chips remain operational even if the host running procedure is offline, earning them lucrative attack vectors to deploy persistent malware.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount

A transient explainer of each and every of the vulnerabilities is below –
- CVE-2023-40284, CVE-2023-40287, and CVE-2023-40288 (CVSS scores: 9.6) – A few cross-web site scripting (XSS) flaws that let remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of the logged-in BMC user.
- CVE-2023-40285 and CVE-2023-40286 (CVSS rating: 8.6) – Two cross-internet site scripting (XSS) flaws that make it possible for distant, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of the logged-in BMC user by poisoning browser cookies or regional storage.
- CVE-2023-40289 (CVSS score: 9.1) – An operating method command injection flaw that enables for the execution of destructive code as a person with administrative privileges.
- CVE-2023-40290 (CVSS rating: 8.3) – A cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw that makes it possible for remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of the logged-in BMC person, but only when working with Internet Explorer 11 browser on Windows.
CVE-2023-40289 is “critical simply because it lets authenticated attackers to acquire root entry and wholly compromise the BMC procedure,” Binarly reported in a complex examination published this week.
“This privilege allows to make the attack persistent even even though the BMC ingredient is rebooted and to transfer laterally within the compromised infrastructure, infecting other endpoints.”
The other six vulnerabilities – CVE-2023-40284, CVE-2023-40287, and CVE-2023-40288 in certain – could be applied to produce an account with admin privileges for the web server ingredient of the BMC IPMI program.
As a end result, a distant attacker searching to consider regulate of the servers could combine them with CVE-2023-40289 to accomplish command injection and reach code execution. In a hypothetical circumstance, this could perform in the form of sending a phishing email bearing a booby-trapped link to the administrator’s email handle that, when clicked, triggers the execution of the XSS payload.

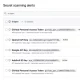
There is presently no proof of any destructive exploitation of the vulnerabilities in the wild, although Binarly mentioned it noticed more than 70,000 cases of internet-exposed Supermicro IPMI web interfaces at the start off of Oct 2023.
“Initial, it is achievable to remotely compromise the BMC procedure by exploiting vulnerabilities in the Web Server element exposed to the internet,” the firmware security business discussed.
“An attacker can then gain access to the Server’s functioning procedure by means of reputable iKVM remote handle BMC operation or by flashing the UEFI of the focus on procedure with destructive firmware that makes it possible for persistent manage of the host OS. From there, practically nothing prevents an attacker from lateral movement in just the internal network, compromising other hosts.”
Earlier this year, two security flaws had been disclosed in AMI MegaRAC BMCs that, if successfully exploited, could enable menace actors to remotely commandeer susceptible servers and deploy malware.
Observed this report appealing? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to go through a lot more distinctive content we write-up.
Some elements of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 QakBot Threat Actors Still in Action, Using Ransom Knight and Remcos RAT in Latest Attacks
QakBot Threat Actors Still in Action, Using Ransom Knight and Remcos RAT in Latest Attacks