The UK govt continues to alter its cyber reaction to the developing menace posed by country-condition adversaries, in line with its latest Countrywide Cyber Strategy (NCS), released in December 2022.
Right after introducing the National Protecting Security Authority (NPSA), a new MI5-hosted company tasked with tackling state-sponsored threats to UK companies, as component of its March 2023 Built-in Assessment Refresh (IRR), the government now made the decision to open up on its offensive cyber abilities.
The Nationwide Cyber Force (NCF), a partnership amongst GCHQ and the Ministry of Defence (MoD) which carries out cyber functions to protect from threats to the UK, shared the rules under which it conducts covert offensive cyber operations in a initial-of-its-sort manual posted on April 4.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
Prior to outlining some ideas ruling how the UK makes use of its offensive cyber capabilities to answer to cyber and physical threats, the NCF shared some caveats to its own great importance.
First, it stated that the agency “would almost never if ever get involved” wherever other responses are much better suited to offer with the problem proficiently.
Also, the NCF acknowledged that cyber operations are not likely to be decisive on their personal and ought to be built-in into a broader reaction method.
Having said that, the agency also outlined why offensive cyber strikes can be a beneficial tool:
- It can at times present the only sensible usually means of disrupting an adversary’s capability to exploit the internet and digital technology.
- It can be exactly specific with precise result and avoid the problems of making use of other, most likely physically damaging, interventions.
- It can generate a selection of cognitive effects – these as undermining an adversary’s self-confidence in the knowledge they are receiving or in the skill of their data programs to perform proficiently – that may well be more durable to obtain with other ways.
Even though these benefits could sound apparent to some, recognizing this in a authorities document can be found as a stage ahead in the states’ accountability in cyberspace.
In the main portion of the guideline, the NCF explained its cyber operations abide by a established of 3 concepts: they want to be accountable, specific and calibrated.
They are also dominated by the ‘doctrine of cognitive outcome,’ which implies that the UK takes advantage of its cyber electricity to limit or have an impact on the information and facts obtainable to an adversary and sap their self-assurance in their technology and the information and facts it delivers.
“Our operate can incorporate covert operations towards the IT networks or technology made use of by adversaries and utilizing techniques to make that technology function significantly less successfully or stop to functionality altogether,” the NCF famous, for case in point.
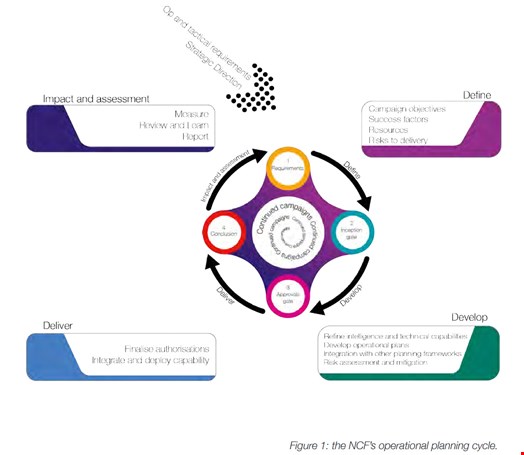 Source: UK governing administration
Source: UK governing administration
The document was also an opportunity for the UK to insist that the NCF operates in a accountable and ethical way and that its functions are carried out primarily based on a legal framework, with their affect thoroughly assessed for both equally escalation and de-escalation.
“In outlining its existing thinking, the NCF aims to promote constructive debate and add to demonstrating the UK’s motivation to currently being a responsible cyber power. It may perhaps also most likely lead to deterrence,” reads the doc.
Sir Jeremy Fleming, GCHQ’s director, mentioned that the guide could pave the way for more cooperation concerning states, or even a upcoming cyber-coalition of international locations. “With the danger expanding and the stakes increased than ever in advance of, we hope this doc gives a benchmark for the UK’s technique and a basis for like-minded governments to come jointly internationally to set up a shared eyesight and values for the dependable use of cyber functions,” he stated in a general public statement.
Declared in 2018 and formally proven as a GCHQ-MoD joint agency in 2020 primarily based on the preceding Nationwide Offensive Cyber Programme, the NCF now draws jointly personnel from GCHQ and the MOD, like Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (DSTL) and UK’s Key Intelligence Company (SIS/MI6) below a single unified command.
It’s the first time the UK government has disclosed any specifics about how the company operates.
Some areas of this report are sourced from:
www.infosecurity-journal.com


 FBI Leads International Effort to Seize Domains for Notorious Genesis Market
FBI Leads International Effort to Seize Domains for Notorious Genesis Market