A security vulnerability has been disclosed in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress that could empower unauthenticated customers to escalate their privileges.
Tracked as CVE-2023-40000, the vulnerability was dealt with in October 2023 in version 5.7..1.
“This plugin suffers from unauthenticated web-site-huge saved [cross-site scripting] vulnerability and could allow for any unauthenticated person from thieving delicate information and facts to, in this situation, privilege escalation on the WordPress web page by performing a one HTTP ask for,” Patchstack researcher Rafie Muhammad reported.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
LiteSpeed Cache, which is utilised to improve web site effectiveness, has additional than five million installations. The newest edition of the plugin in 6.1, which was released on February 5, 2024.

The WordPress security corporation mentioned CVE-2023-40000 is the final result of a lack of consumer enter sanitization and escaping output. The vulnerability is rooted in a functionality named update_cdn_position() and can be reproduced in a default set up.
“Considering the fact that the XSS payload is placed as an admin discover and the admin detect could be shown on any wp-admin endpoint, this vulnerability also could be simply triggered by any user that has access to the wp-admin region,” Muhammad explained.
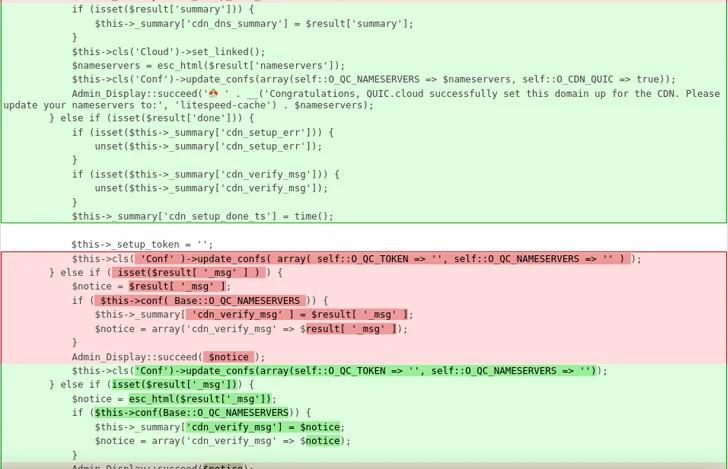
The disclosure arrives 4 months soon after Wordfence revealed yet another XSS flaw in the identical plugin (CVE-2023-4372, CVSS rating: 6.4) because of to insufficient enter sanitization and output escaping on consumer provided characteristics. It was tackled in version 5.7.
“This can make it doable for authenticated attackers with contributor-amount and higher than permissions to inject arbitrary web scripts in internet pages that will execute every time a user accesses an injected webpage,” István Márton claimed.
Identified this posting attention-grabbing? Observe us on Twitter and LinkedIn to study extra exclusive information we submit.
Some areas of this article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Open-Source Xeno RAT Trojan Emerges as a Potent Threat on GitHub
Open-Source Xeno RAT Trojan Emerges as a Potent Threat on GitHub