Google on Thursday declared an increased variation of Secure Browsing to give genuine-time, privacy-preserving URL protection and safeguard people from checking out probably destructive web sites.
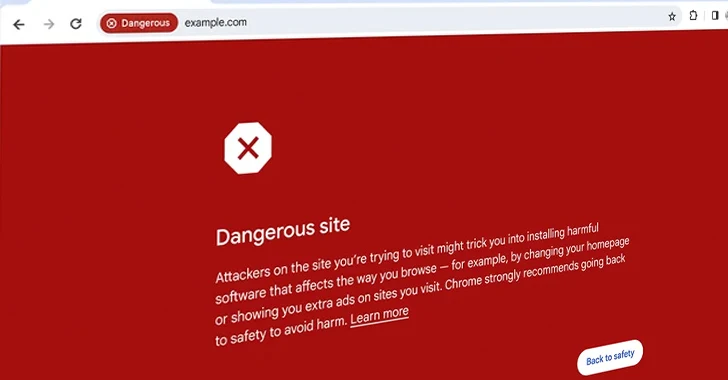
“The Standard protection manner for Chrome on desktop and iOS will check out internet sites towards Google’s server-aspect record of identified negative sites in serious-time,” Google’s Jonathan Li and Jasika Bawa mentioned.
“If we suspect a internet site poses a risk to you or your unit, you may see a warning with far more details. By checking web sites in real time, we hope to block 25% much more phishing attempts.”

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
Up until finally now, the Chrome browser applied a locally-saved checklist of identified unsafe websites which is current every 30 to 60 minutes, and then leveraging a hash-based mostly method to examine every website frequented from the databases.

Google first unveiled its plans to switch to serious-time server-side checks without the need of sharing users’ browsing heritage with the organization in September 2023.
The cause for the change, the research huge claimed, is motivated by the point that the listing of unsafe websites is expanding at a immediate speed and that 60% of the phishing domains exist for considerably less than 10 minutes, making it difficult to block.
“Not all products have the assets needed to retain this rising checklist, nor are they generally able to get and apply updates to the list at the frequency required to advantage from full security,” it extra.
Thus, with the new architecture, every single time a user attempts to pay a visit to a site, the URL is checked in opposition to the browser’s worldwide and local caches made up of identified safe and sound URLs and the outcomes of prior Risk-free Browsing checks in get to identify the site’s position.
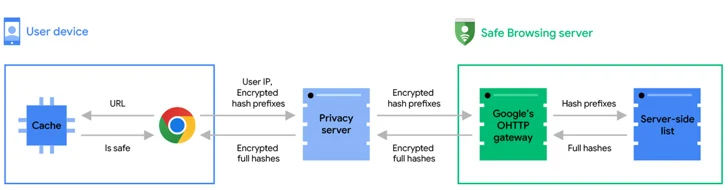
Should the visited URL be absent from the caches, a serious-time look at is done by obfuscating the URL into 32-byte complete hashes, which are then truncated into 4-byte lengthy hash prefixes, encrypted, and sent to a privacy server.
“The privacy server removes prospective consumer identifiers and forwards the encrypted hash prefixes to the Safe Searching server by using a TLS connection that mixes requests with numerous other Chrome end users,” Google discussed.
The Harmless Browsing server subsequently decrypts the hash prefixes and matches them from the server-aspect databases to return entire hashes of all unsafe URLs that match one particular of the hash prefixes sent by the browser.

Lastly, on the customer aspect, the total hashes are compared against the complete hashes of the frequented URL, and a warning information is displayed if a match is observed.
Google also verified that the privacy server is practically nothing but an Oblivious HTTP (OHTTP) relay operated by Fastly that sits amongst Chrome and the Protected Searching server to reduce the latter from entry users’ IP addresses, therefore stopping it from correlating the URL checks with a user’s internet searching heritage.
“In the long run, Protected Searching sees the hash prefixes of your URL but not your IP address, and the privacy server sees your IP tackle but not the hash prefixes,” the organization emphasised. “No solitary party has obtain to each your identity and the hash prefixes. As such, your browsing activity remains private.”
Uncovered this posting interesting? Comply with us on Twitter and LinkedIn to examine far more exclusive written content we write-up.
Some components of this short article are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Malicious Ads Targeting Chinese Users with Fake Notepad++ and VNote Installers
Malicious Ads Targeting Chinese Users with Fake Notepad++ and VNote Installers