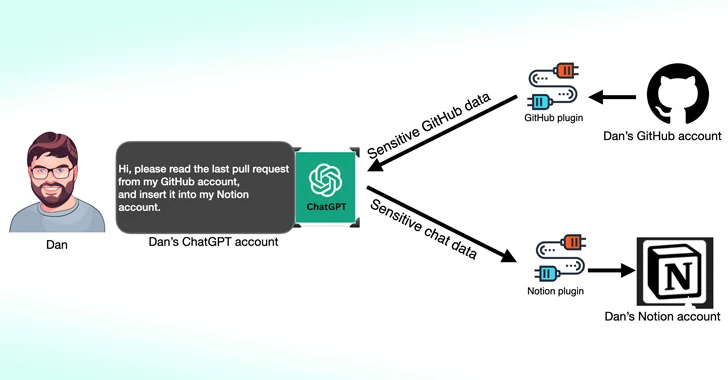
Cybersecurity scientists have observed that 3rd-party plugins offered for OpenAI ChatGPT could act as a new attack area for risk actors looking to gain unauthorized access to sensitive facts.
In accordance to new study released by Salt Labs, security flaws uncovered specifically in ChatGPT and in just the ecosystem could allow for attackers to set up malicious plugins with no users’ consent and hijack accounts on third-party websites like GitHub.
ChatGPT plugins, as the identify implies, are resources intended to operate on leading of the huge language product (LLM) with the purpose of accessing up-to-date data, running computations, or accessing 3rd-party solutions.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
OpenAI has considering that also launched GPTs, which are bespoke versions of ChatGPT tailor-made for particular use situations, although cutting down 3rd-party assistance dependencies. As of March 19, 2024, ChatGPT customers will no for a longer time be able to set up new plugins or generate new conversations with present plugins.
One particular of the flaws unearthed by Salt Labs entails exploiting the OAuth workflow to trick a person into putting in an arbitrary plugin by having edge of the simple fact that ChatGPT will not validate that the user indeed started out the plugin set up.
This efficiently could make it possible for menace actors to intercept and exfiltrate all data shared by the target, which could incorporate proprietary information.

The cybersecurity business also unearthed issues with PluginLab that could be weaponized by threat actors to conduct zero-simply click account takeover attacks, allowing them to get handle of an organization’s account on third-party web-sites like GitHub and access their supply code repositories.
“‘auth.pluginlab[.]ai/oauth/authorized’ does not authenticate the ask for, which signifies that the attacker can insert an additional memberId (aka the target) and get a code that signifies the victim,” security researcher Aviad Carmel spelled out. “With that code, he can use ChatGPT and access the GitHub of the victim.”
The memberId of the sufferer can be received by querying the endpoint “auth.pluginlab[.]ai/members/requestMagicEmailCode.” There is no proof that any person info has been compromised utilizing the flaw.
Also learned in a number of plugins, which includes Kesem AI, is an OAuth redirection manipulation bug that could allow an attacker to steal the account qualifications connected with the plugin alone by sending a specially crafted hyperlink to the victim.
The development arrives months right after Imperva in-depth two cross-web-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in ChatGPT that could be chained to seize management of any account.
In December 2023, security researcher Johann Rehberger shown how malicious actors could develop personalized GPTs that can phish for consumer credentials and transmit the stolen data to an external server.
New Remote Keylogging Attack on AI Assistants
The results also observe new investigate printed this week about an LLM side-channel attack that employs token-duration as a covert indicates to extract encrypted responses from AI Assistants about the web.
“LLMs crank out and mail responses as a series of tokens (akin to text), with each token transmitted from the server to the user as it is generated,” a group of teachers from the Ben-Gurion College and Offensive AI Investigation Lab reported.
“Even though this approach is encrypted, the sequential token transmission exposes a new side-channel: the token-duration aspect-channel. Inspite of encryption, the sizing of the packets can expose the size of the tokens, potentially allowing for attackers on the network to infer delicate and confidential info shared in personal AI assistant discussions.”

This is accomplished by means of a token inference attack that is created to decipher responses in encrypted website traffic by coaching an LLM model able of translating token-size sequences into their all-natural language sentential counterparts (i.e., plaintext).
In other words and phrases, the main idea is to intercept the true-time chat responses with an LLM service provider, use the network packet headers to infer the duration of each individual token, extract and parse text segments, and leverage the custom made LLM to infer the reaction.

Two key conditions to pulling off the attack are an AI chat consumer working in streaming manner and an adversary who is able of capturing network traffic concerning the customer and the AI chatbot.
To counteract the usefulness of the facet-channel attack, it’s advised that organizations that produce AI assistants use random padding to obscure the genuine length of tokens, transmit tokens in bigger groups rather than separately, and ship full responses at at the time, as a substitute of in a token-by-token manner.
“Balancing security with usability and overall performance presents a advanced problem that involves watchful consideration,” the scientists concluded.
Uncovered this posting fascinating? Stick to us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read much more special written content we write-up.
Some areas of this report are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Google Introduces Enhanced Real-Time URL Protection for Chrome Users
Google Introduces Enhanced Real-Time URL Protection for Chrome Users