Cybersecurity scientists disclosed information about 13 vulnerabilities in the Nagios network checking application that could be abused by an adversary to hijack the infrastructure devoid of any operator intervention.
“In a telco setting, in which a telco is checking countless numbers of web sites, if a purchaser web site is completely compromised, an attacker can use the vulnerabilities to compromise the telco, and then each other monitored shopper web page,” Adi Ashkenazy, CEO of Australian cybersecurity organization Skylight Cyber, advised The Hacker News by using email.
Nagios is an open-resource IT infrastructure device analogous to SolarWinds Network General performance Monitor (NPM) that features monitoring and alerting expert services for servers, network cards, applications, and expert services.

Protect your privacy by Mullvad VPN. Mullvad VPN is one of the famous brands in the security and privacy world. With Mullvad VPN you will not even be asked for your email address. No log policy, no data from you will be saved. Get your license key now from the official distributor of Mullvad with discount: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Get Mullvad VPN with 12% Discount
The issues, which consist of a blend of authenticated remote code execution (RCE) and privilege escalation flaws, had been learned and claimed to Nagios in Oct 2020, following which they were remediated in November.

Main between them is CVE-2020-28648 (CVSS score: 8.8), which problems an incorrect input validation in the Automobile-Discovery element of Nagios XI that the researchers made use of as a leaping-off point to set off an exploit chain that strings jointly a full of 5 vulnerabilities to attain a “effective upstream attack.”
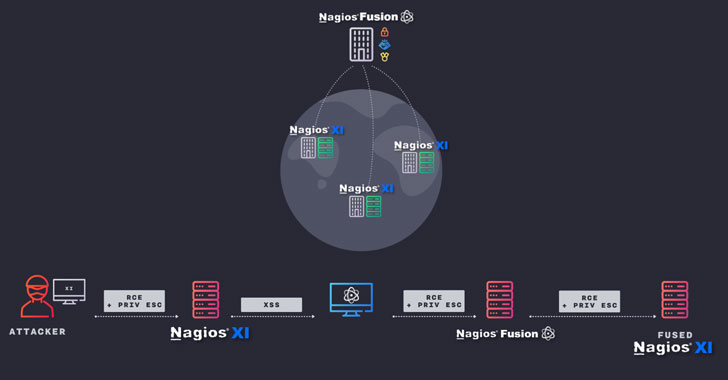
“Specifically, if we, as attackers, compromise a customer web page that is remaining monitored utilizing a Nagios XI server, we can compromise the telecommunications company’s administration server and each other buyer that is currently being monitored,” the scientists claimed in a generate-up revealed very last 7 days.
Put in different ways the attack situation will work by targeting a Nagios XI server at the shopper internet site, employing CVE-2020-28648 and CVE-2020-28910 to get RCE and elevate privileges to “root.” With the server now successfully compromised, the adversary can then mail tainted information to the upstream Nagios Fusion server that’s used to give centralized infrastructure-wide visibility by periodically polling the Nagios XI servers.
“By tainting information returned from the XI server less than our management we can trigger Cross-Web-site Scripting [CVE-2020-28903] and execute JavaScript code in the context of a Fusion person,” Skylight Cyber researcher Samir Ghanem claimed.
The subsequent section of the attack leverages this skill to run arbitrary JavaScript code on the Fusion server to get RCE (CVE-2020-28905) and subsequently elevate permissions (CVE-2020-28902) to seize command of the Fusion server and, in the end, crack into XI servers located at other buyer internet sites.
The researchers have also printed a PHP-based article-exploitation software identified as SoyGun that chains the vulnerabilities collectively and “will allow an attacker with Nagios XI user’s qualifications and HTTP access to the Nagios XI server to acquire entire command of a Nagios Fusion deployment.”
A summary of the 13 vulnerabilities is mentioned beneath –
- CVE-2020-28648 – Nagios XI authenticated remote code execution (from the context of a lower-privileged consumer)
- CVE-2020-28900 – Nagios Fusion and XI privilege escalation from nagios to root by using enhance_to_most recent.sh
- CVE-2020-28901 – Nagios Fusion privilege escalation from apache to nagios by way of command injection on ingredient_dir parameter in cmd_subsys.php
- CVE-2020-28902 – Nagios Fusion privilege escalation from apache to nagios by means of command injection on timezone parameter in cmd_subsys.php
- CVE-2020-28903 – XSS in Nagios XI when an attacker has regulate over a fused server
- CVE-2020-28904 – Nagios Fusion privilege escalation from apache to nagios by using the installation of malicious parts
- CVE-2020-28905 – Nagios Fusion authenticated distant code execution (from the context of reduced-privileges user)
- CVE-2020-28906 – Nagios Fusion and XI privilege escalation from nagios to root via modification of fusion-sys.cfg / xi-sys.cfg
- CVE-2020-28907 – Nagios Fusion privilege escalation from apache to root through up grade_to_hottest.sh and modification of proxy config
- CVE-2020-28908 – Nagios Fusion privilege escalation from apache to nagios by means of command injection (induced by lousy sanitization) in cmd_subsys.php
- CVE-2020-28909 – Nagios Fusion privilege escalation from nagios to root through modification of scripts that can execute as sudo
- CVE-2020-28910 – Nagios XI getprofile.sh privilege escalation
- CVE-2020-28911 – Nagios Fusion information disclosure: Decrease privileged person can authenticate to fused server when credentials are stored
With SolarWinds falling victim to a big provide chain attack very last 12 months, focusing on a network checking platform like Nagios could empower a destructive actor to orchestrate intrusions into corporate networks, laterally grow their entry throughout the IT network, and become an entry place for a lot more innovative threats.
“The volume of energy that was demanded to locate these vulnerabilities and exploit them is negligible in the context of innovative attackers, and particularly nation-states,” Ghanem explained.
“If we could do it as a brief facet task, visualize how simple this is for people who devote their total time to produce these styles of exploits. Compound that with the number of libraries, instruments and distributors that are present and can be leveraged in a modern day network, and we have a main issue on our arms.”
Found this post interesting? Stick to THN on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn to read much more special written content we post.
Some elements of this post are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 FBI Analyst Charged With Stealing Counterterrorism and Cyber Threats Info
FBI Analyst Charged With Stealing Counterterrorism and Cyber Threats Info