Graphic Source: Toptal
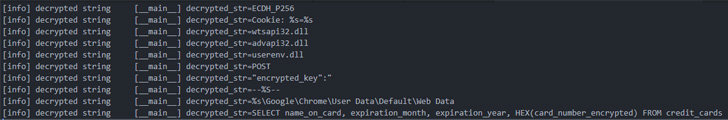
The infamous Emotet malware has turned to deploy a new module designed to siphon credit history card information saved in the Chrome web browser.
The credit card stealer, which completely singles out Chrome, has the capability to exfiltrate the collected info to unique remote command-and-manage (C2) servers, in accordance to enterprise security enterprise Proofpoint, which noticed the component on June 6.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
The advancement arrives amid a spike in Emotet exercise given that it was resurrected late final calendar year next a 10-thirty day period-extended hiatus in the wake of a legislation enforcement operation that took down its attack infrastructure in January 2021.
Emotet, attributed to a danger actor recognised as TA542 (aka Mummy Spider or Gold Crestwood), is an state-of-the-art, self-propagating and modular trojan that is shipped via email strategies and is utilised as a distributor for other payloads these as ransomware.

As of April 2022, Emotet is even now the most preferred malware with a world impression of 6% of businesses worldwide, adopted by Formbook and Agent Tesla, for every Verify Level, with the malware testing out new delivery approaches working with OneDrive URLs and PowerShell in .LNK attachments to get all over Microsoft’s macro limitations.
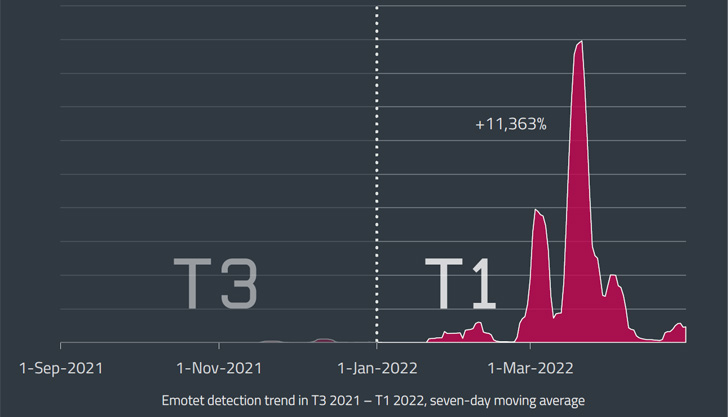
The continual progress in Emotet-linked threats is substantiated additional by the truth that the quantity of phishing e-mail, frequently hijacking previously current correspondence, grew from 3,000 in February 2022 to somewhere around 30,000 in March targeting companies in various nations around the world as aspect of a mass-scale spam campaign.
Stating that Emotet action have “shifted to a increased gear” in March and April 2022, ESET claimed that detections jumped a 100-fold, registering a advancement of over 11,000% all through the to start with four months of the year when in contrast to the preceding three-thirty day period period from September to December 2021.
Some of the typical targets given that the botnet’s resurrection have been Japan, Italy, and Mexico, the Slovak cybersecurity firm pointed out, introducing the largest wave was recorded on March 16, 2022.
“The measurement of Emotet’s newest LNK and XLL campaigns was appreciably smaller sized than individuals dispersed by means of compromised DOC data files noticed in March,” Dušan Lacika, senior detection engineer at Dušan Lacika, said.

“This indicates that the operators are only applying a portion of the botnet’s likely though testing new distribution vectors that could substitute the now disabled-by-default VBA macros.”
The conclusions also come as scientists from CyberArk shown a new approach to extract plaintext qualifications instantly from memory in Chromium-based mostly web browsers.
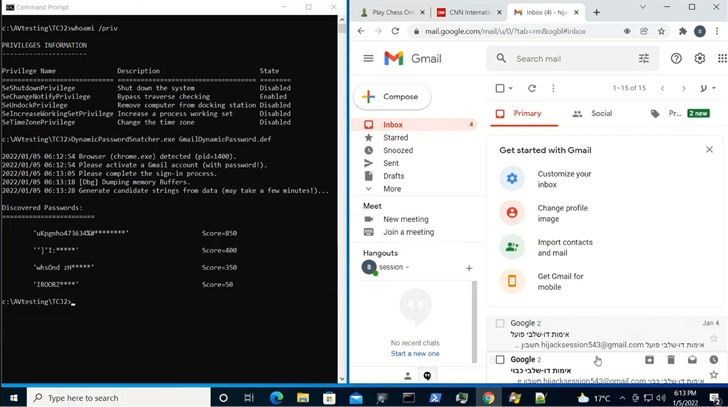
“Credential details is stored in Chrome’s memory in cleartext structure,” CyberArk’s Zeev Ben Porat mentioned. “In addition to information that is dynamically entered when signing into unique web programs, an attacker can cause the browser to load into memory all the passwords that are stored in the password manager.”
This also involves cookie-associated details these types of as session cookies, probably allowing for an attacker to extract the information and use it to hijack users’ accounts even when they are guarded by multi-factor authentication.
Uncovered this short article interesting? Stick to THN on Fb, Twitter and LinkedIn to study additional exclusive articles we article.
Some components of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com


 #RSAC: Current Nation-State and Ransomware Gang Threat Trends
#RSAC: Current Nation-State and Ransomware Gang Threat Trends