Proof-of-strategy (Poc) code has been produced for a now-patched significant-severity security flaw in the Windows CryptoAPI that the U.S. National Security Company (NSA) and the U.K. Countrywide Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) documented to Microsoft past yr.
Tracked as CVE-2022-34689 (CVSS rating: 7.5), the spoofing vulnerability was dealt with by the tech giant as section of Patch Tuesday updates introduced in August 2022, but was only publicly disclosed two months later on on Oct 11, 2022.
“An attacker could manipulate an existing public x.509 certificate to spoof their id and carry out steps this sort of as authentication or code signing as the qualified certificate,” Microsoft mentioned in an advisory introduced at the time.

Protect and backup your data using AOMEI Backupper. AOMEI Backupper takes secure and encrypted backups from your Windows, hard drives or partitions. With AOMEI Backupper you will never be worried about loosing your data anymore.
Get AOMEI Backupper with 72% discount from an authorized distrinutor of AOMEI: SerialCart® (Limited Offer).
➤ Activate Your Coupon Code
The Windows CryptoAPI features an interface for builders to add cryptographic companies such as encryption/decryption of details and authentication working with digital certificates to their apps.
Web security enterprise Akamai, which introduced the PoC, reported CVE-2022-34689 is rooted in the point that the vulnerable piece of code which is intended to acknowledge an x.509 certificate carried out a test that exclusively relied on the certificate’s MD5 fingerprint.
MD5, a message-digest algorithm used for hashing, is fundamentally cryptographically damaged as of December 2008 owing to the risk of birthday attacks, a cryptanalytic strategy employed to uncover collisions in a hash operate.
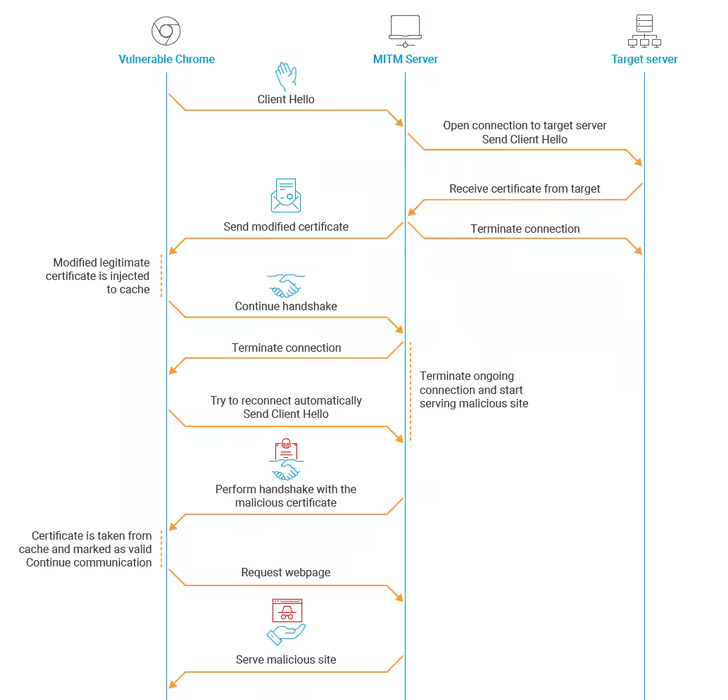
The net influence of this shortcoming is that it opens the doorway for a undesirable actor to provide a modified version of a respectable certificate to a victim application, and then create a new certification whose MD5 hash collides with the rigged certificate and use it to masquerade as the primary entity.
In other phrases, the flaw could be weaponized by a rogue interloper to stage a mallory-in-the-middle (MitM) attack and redirect consumers relying on an aged variation of Google Chrome (model 48 and earlier) to an arbitrary web page of the actor’s picking only for the reason that the inclined edition of the web browser trusts the destructive certificate.
“Certificates perform a key position in identity verification online, earning this vulnerability worthwhile for attackers,” Akamai explained.
Whilst the flaw has a confined scope, the Massachusetts-headquartered agency pointed out “there is nonetheless a great deal of code that makes use of this API and could be exposed to this vulnerability, warranting a patch even for discontinued versions of Windows, like Windows 7.”
Discovered this short article attention-grabbing? Abide by us on Twitter and LinkedIn to browse additional exceptional written content we write-up.
Some elements of this posting are sourced from:
thehackernews.com

 Researchers Uncover Connection b/w Moses Staff and Emerging Abraham’s Ax Hacktivists Group
Researchers Uncover Connection b/w Moses Staff and Emerging Abraham’s Ax Hacktivists Group